Page 415 - Handbook of Energy Engineering Calculations
P. 415
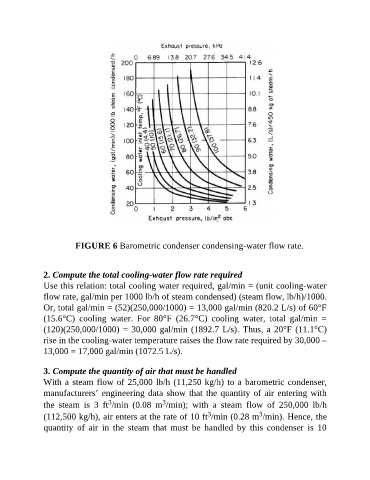
FIGURE 6 Barometric condenser condensing-water flow rate.
2. Compute the total cooling-water flow rate required
Use this relation: total cooling water required, gal/min = (unit cooling-water
flow rate, gal/min per 1000 lb/h of steam condensed) (steam flow, lb/h)/1000.
Or, total gal/min = (52)(250,000/1000) = 13,000 gal/min (820.2 L/s) of 60°F
(15.6°C) cooling water. For 80°F (26.7°C) cooling water, total gal/min =
(120)(250,000/1000) = 30,000 gal/min (1892.7 L/s). Thus, a 20°F (11.1°C)
rise in the cooling-water temperature raises the flow rate required by 30,000 –
13,000 = 17,000 gal/min (1072.5 L/s).
3. Compute the quantity of air that must be handled
With a steam flow of 25,000 lb/h (11,250 kg/h) to a barometric condenser,
manufacturers’ engineering data show that the quantity of air entering with
3
3
the steam is 3 ft /min (0.08 m /min); with a steam flow of 250,000 lb/h
3
3
(112,500 kg/h), air enters at the rate of 10 ft /min (0.28 m /min). Hence, the
quantity of air in the steam that must be handled by this condenser is 10