Page 414 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 414
412 CHAPTER 16 Degradation of protective PVD coatings
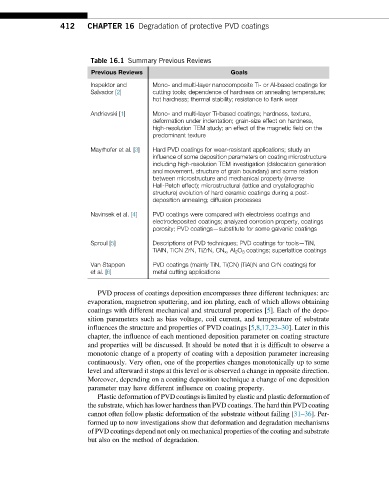
Table 16.1 Summary Previous Reviews
Previous Reviews Goals
Inspektor and Mono- and multi-layer nanocomposite Ti- or Al-based coatings for
Salvador [2] cutting tools; dependence of hardness on annealing temperature;
hot hardness; thermal stability; resistance to flank wear
Andrievski [1] Mono- and multi-layer Ti-based coatings; hardness, texture,
deformation under indentation; grain-size effect on hardness,
high-resolution TEM study; an effect of the magnetic field on the
predominant texture
Mayrhofer et al. [3] Hard PVD coatings for wear-resistant applications; study an
influence of some deposition parameters on coating microstructure
including high-resolution TEM investigation (dislocation generation
and movement, structure of grain boundary) and some relation
between microstructure and mechanical property (inverse
Hall-Petch effect); microstructural (lattice and crystallographic
structure) evolution of hard ceramic coatings during a post-
deposition annealing; diffusion processes
Navinsek et al. [4] PVD coatings were compared with electroless coatings and
electrodeposited coatings; analyzed corrosion property, coatings
porosity; PVD coatings—substitute for some galvanic coatings
Sproul [5] Descriptions of PVD techniques; PVD coatings for tools—TiN,
TiAlN, TiCN ZrN, TiZrN, CN x ,Al 2 O 3 coatings; superlattice coatings
Van Stappen PVD coatings (mainly TiN, Ti(CN) (TiAl)N and CrN coatings) for
et al. [6] metal cutting applications
PVD process of coatings deposition encompasses three different techniques: arc
evaporation, magnetron sputtering, and ion plating, each of which allows obtaining
coatings with different mechanical and structural properties [5]. Each of the depo-
sition parameters such as bias voltage, coil current, and temperature of substrate
influences the structure and properties of PVD coatings [5,8,17,23–30]. Later in this
chapter, the influence of each mentioned deposition parameter on coating structure
and properties will be discussed. It should be noted that it is difficult to observe a
monotonic change of a property of coating with a deposition parameter increasing
continuously. Very often, one of the properties changes monotonically up to some
level and afterward it stops at this level or is observed a change in opposite direction.
Moreover, depending on a coating deposition technique a change of one deposition
parameter may have different influence on coating property.
Plastic deformation of PVD coatings is limited by elastic and plastic deformation of
the substrate, which has lower hardness than PVD coatings. The hard thin PVD coating
cannot often follow plastic deformation of the substrate without failing [31–36]. Per-
formed up to now investigations show that deformation and degradation mechanisms
of PVD coatings depend not only on mechanical properties of the coating and substrate
but also on the method of degradation.