Page 77 - Handbook of Natural Gas Transmission and Processing Principles and Practices
P. 77
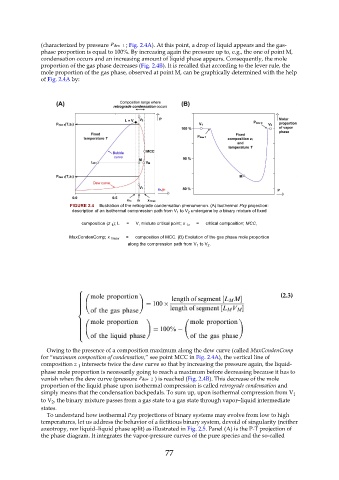
(characterized by pressure ; Fig. 2.4A). At this point, a drop of liquid appears and the gas-
phase proportion is equal to 100%. By increasing again the pressure up to, e.g., the one of point M,
condensation occurs and an increasing amount of liquid phase appears. Consequently, the mole
proportion of the gas phase decreases (Fig. 2.4B). It is recalled that according to the lever rule, the
mole proportion of the gas phase, observed at point M, can be graphically determined with the help
of Fig. 2.4A by:
FIGURE 2.4 Illustration of the retrograde condensation phenomenon. (A) Isothermal Pxy projection:
description of an isothermal compression path from V 1 to V 2 undergone by a binary mixture of fixed
composition (z 1 ); L = V, mixture critical point; x 1c = critical composition; MCC,
MaxCondenComp; x 1max = composition of MCC. (B) Evolution of the gas phase mole proportion
along the compression path from V 1 to V 2 .
(2.3)
Owing to the presence of a composition maximum along the dew curve (called MaxCondenComp
for “maximum composition of condensation,” see point MCC in Fig. 2.4A), the vertical line of
composition z intersects twice the dew curve so that by increasing the pressure again, the liquid-
1
phase mole proportion is necessarily going to reach a maximum before decreasing because it has to
vanish when the dew curve (pressure ) is reached (Fig. 2.4B). This decrease of the mole
proportion of the liquid phase upon isothermal compression is called retrograde condensation and
simply means that the condensation backpedals. To sum up, upon isothermal compression from V 1
to V , the binary mixture passes from a gas state to a gas state through vapor–liquid intermediate
2
states.
To understand how isothermal Pxy projections of binary systems may evolve from low to high
temperatures, let us address the behavior of a fictitious binary system, devoid of singularity (neither
azeotropy, nor liquid–liquid phase split) as illustrated in Fig. 2.5. Panel (A) is the P-T projection of
the phase diagram. It integrates the vapor-pressure curves of the pure species and the so-called
77