Page 162 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 162
THERMOSETS
3.32 CHAPTER 3
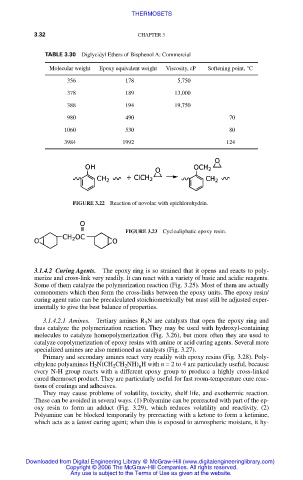
TABLE 3.30 Diglycidyl Ethers of Bisphenol A: Commercial
Molecular weight Epoxy equivalent weight Viscosity, cP Softening point, °C
356 178 5,750
378 189 13,000
388 194 19,750
980 490 70
1060 530 80
3984 1992 124
FIGURE 3.22 Reaction of novolac with epichlorohydrin.
FIGURE 3.23 Cycloaliphatic epoxy resin.
3.1.4.2 Curing Agents. The epoxy ring is so strained that it opens and reacts to poly-
merize and cross-link very readily. It can react with a variety of basic and acidic reagents.
Some of them catalyze the polymerization reaction (Fig. 3.25). Most of them are actually
comonomers which then form the cross-links between the epoxy units. The epoxy resin/
curing agent ratio can be precalculated stoichiometrically but must still be adjusted exper-
imentally to give the best balance of properties.
3.1.4.2.1 Amines. Tertiary amines R N are catalysts that open the epoxy ring and
3
thus catalyze the polymerization reaction. They may be used with hydroxyl-containing
molecules to catalyze homopolymerization (Fig. 3.26), but more often they are used to
catalyze copolymerization of epoxy resins with amine or acid curing agents. Several more
specialized amines are also mentioned as catalysts (Fig. 3.27).
Primary and secondary amines react very readily with epoxy resins (Fig. 3.28). Poly-
ethylene polyamines H N(CH CH NH) H with n = 2 to 4 are particularly useful, because
2
2
2
n
every N-H group reacts with a different epoxy group to produce a highly cross-linked
cured thermoset product. They are particularly useful for fast room-temperature cure reac-
tions of coatings and adhesives.
They may cause problems of volatility, toxicity, shelf life, and exothermic reaction.
These can be avoided in several ways. (1) Polyamine can be prereacted with part of the ep-
oxy resin to form an adduct (Fig. 3.29), which reduces volatility and reactivity. (2)
Polyamine can be blocked temporarily by prereacting with a ketone to form a ketimine,
which acts as a latent curing agent; when this is exposed to atmospheric moisture, it hy-
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.