Page 166 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 166
THERMOSETS
3.36 CHAPTER 3
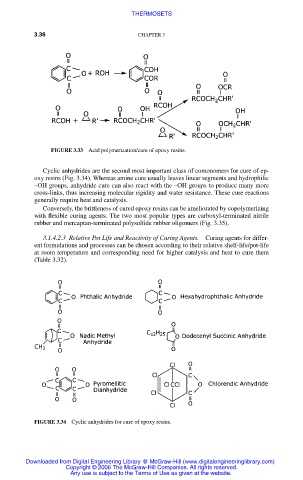
FIGURE 3.33 Acid polymerization/cure of epoxy resins.
Cyclic anhydrides are the second most important class of comonomers for cure of ep-
oxy resins (Fig. 3.34). Whereas amine cure usually leaves linear segments and hydrophilic
–OH groups, anhydride cure can also react with the –OH groups to produce many more
cross-links, thus increasing molecular rigidity and water resistance. These cure reactions
generally require heat and catalysis.
Conversely, the brittleness of cured epoxy resins can be ameliorated by copolymerizing
with flexible curing agents. The two most popular types are carboxyl-terminated nitrile
rubber and mercaptan-terminated polysulfide rubber oligomers (Fig. 3.35).
3.1.4.2.3 Relative Pot Life and Reactivity of Curing Agents. Curing agents for differ-
ent formulations and processes can be chosen according to their relative shelf-life/pot-life
at room temperature and corresponding need for higher catalysis and heat to cure them
(Table 3.32).
FIGURE 3.34 Cyclic anhydrides for cure of epoxy resins.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.