Page 169 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 169
THERMOSETS
THERMOSETS 3.39
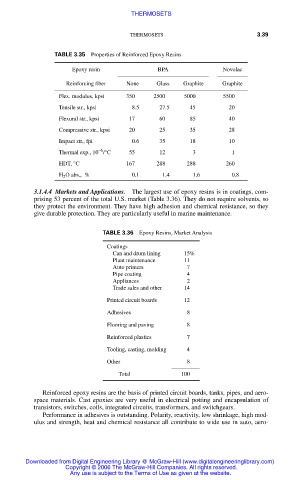
TABLE 3.35 Properties of Reinforced Epoxy Resins
Epoxy resin BPA Novolac
Reinforcing fiber None Glass Graphite Graphite
Flex. modulus, kpsi 350 2500 5000 5500
Tensile str., kpsi 8.5 27.5 45 20
Flexural str., kpsi 17 60 85 40
Compressive str., kpsi 20 25 35 28
Impact str., fpi 0.6 35 18 10
–6
Thermal exp., 10 /°C 55 12 3 1
HDT, °C 167 288 288 260
H O abs., % 0.1 1.4 1.6 0.8
2
3.1.4.4 Markets and Applications. The largest use of epoxy resins is in coatings, com-
prising 53 percent of the total U.S. market (Table 3.36). They do not require solvents, so
they protect the environment. They have high adhesion and chemical resistance, so they
give durable protection. They are particularly useful in marine maintenance.
TABLE 3.36 Epoxy Resins, Market Analysis
Coatings
Can and drum lining 15%
Plant maintenance 11
Auto primers 7
Pipe coating 4
Appliances 2
Trade sales and other 14
Printed circuit boards 12
Adhesives 8
Flooring and paving 8
Reinforced plastics 7
Tooling, casting, molding 4
Other 8
Total 100
Reinforced epoxy resins are the basis of printed circuit boards, tanks, pipes, and aero-
space materials. Cast epoxies are very useful in electrical potting and encapsulation of
transistors, switches, coils, integrated circuits, transformers, and switchgears.
Performance in adhesives is outstanding. Polarity, reactivity, low shrinkage, high mod-
ulus and strength, heat and chemical resistance all contribute to wide use in auto, aero-
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.