Page 164 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 164
THERMOSETS
3.34 CHAPTER 3
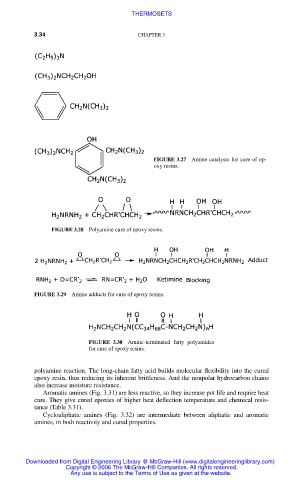
FIGURE 3.27 Amine catalysts for cure of ep-
oxy resins.
FIGURE 3.28 Polyamine cure of epoxy resins.
FIGURE 3.29 Amine adducts for cure of epoxy resins.
FIGURE 3.30 Amine-terminated fatty polyamides
for cure of epoxy resins.
polyamine reaction. The long-chain fatty acid builds molecular flexibility into the cured
epoxy resin, thus reducing its inherent brittleness. And the nonpolar hydrocarbon chains
also increase moisture resistance.
Aromatic amines (Fig. 3.31) are less reactive, so they increase pot life and require heat
cure. They give cured epoxies of higher heat deflection temperature and chemical resis-
tance (Table 3.31).
Cycloaliphatic amines (Fig. 3.32) are intermediate between aliphatic and aromatic
amines, in both reactivity and cured properties.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.