Page 171 - High Power Laser Handbook
P. 171
140 Diode Lasers High-Power Diode Laser Arrays 141
(a) (b)
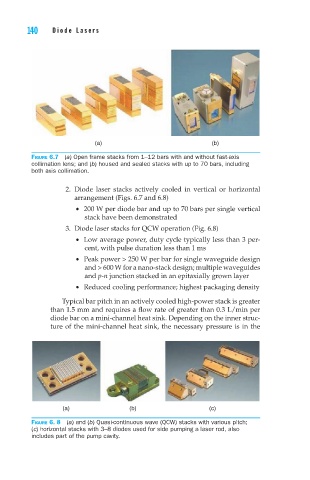
Figure 6.7 (a) Open frame stacks from 1–12 bars with and without fast-axis
collimation lens; and (b) housed and sealed stacks with up to 70 bars, including
both axis collimation.
2. Diode laser stacks actively cooled in vertical or horizontal
arrangement (Figs. 6.7 and 6.8)
• 200 W per diode bar and up to 70 bars per single vertical
stack have been demonstrated
3. Diode laser stacks for QCW operation (Fig. 6.8)
• Low average power, duty cycle typically less than 3 per-
cent, with pulse duration less than 1 ms
• Peak power > 250 W per bar for single waveguide design
and > 600 W for a nano-stack design; multiple waveguides
and p-n junction stacked in an epitaxially grown layer
• Reduced cooling performance; highest packaging density
Typical bar pitch in an actively cooled high-power stack is greater
than 1.5 mm and requires a flow rate of greater than 0.3 L/min per
diode bar on a mini-channel heat sink. Depending on the inner struc-
ture of the mini-channel heat sink, the necessary pressure is in the
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 6. 8 (a) and (b) Quasi-continuous wave (QCW) stacks with various pitch;
(c) horizontal stacks with 3–8 diodes used for side pumping a laser rod, also
includes part of the pump cavity.