Page 142 - Human Inspired Dexterity in Robotic Manipulation
P. 142
Hand Design—Hybrid Soft and Hard Structures 139
(A) (B) (C)
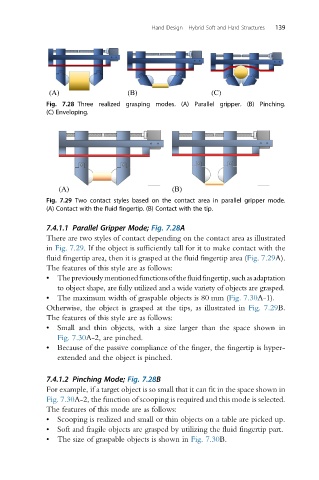
Fig. 7.28 Three realized grasping modes. (A) Parallel gripper. (B) Pinching.
(C) Enveloping.
(A) (B)
Fig. 7.29 Two contact styles based on the contact area in parallel gripper mode.
(A) Contact with the fluid fingertip. (B) Contact with the tip.
7.4.1.1 Parallel Gripper Mode; Fig. 7.28A
There are two styles of contact depending on the contact area as illustrated
in Fig. 7.29. If the object is sufficiently tall for it to make contact with the
fluid fingertip area, then it is grasped at the fluid fingertip area (Fig. 7.29A).
The features of this style are as follows:
• Thepreviouslymentionedfunctionsofthefluidfingertip,suchasadaptation
to object shape, are fully utilized and a wide variety of objects are grasped.
• The maximum width of graspable objects is 80 mm (Fig. 7.30A-1).
Otherwise, the object is grasped at the tips, as illustrated in Fig. 7.29B.
The features of this style are as follows:
• Small and thin objects, with a size larger than the space shown in
Fig. 7.30A-2, are pinched.
• Because of the passive compliance of the finger, the fingertip is hyper-
extended and the object is pinched.
7.4.1.2 Pinching Mode; Fig. 7.28B
For example, if a target object is so small that it can fit in the space shown in
Fig. 7.30A-2, the function of scooping is required and this mode is selected.
The features of this mode are as follows:
• Scooping is realized and small or thin objects on a table are picked up.
• Soft and fragile objects are grasped by utilizing the fluid fingertip part.
• The size of graspable objects is shown in Fig. 7.30B.