Page 79 - Hybrid-Renewable Energy Systems in Microgrids
P. 79
Multilevel inverters: an enabling technology 63
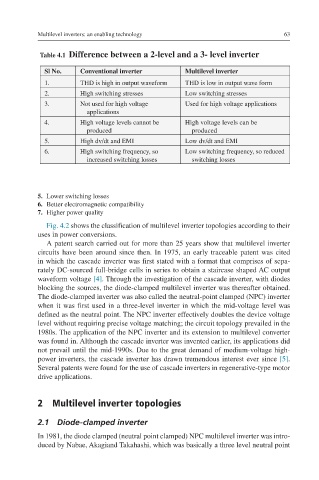
Table 4.1 Difference between a 2-level and a 3- level inverter
Sl No. Conventional inverter Multilevel inverter
1. THD is high in output waveform THD is low in output wave form
2. High switching stresses Low switching stresses
3. Not used for high voltage Used for high voltage applications
applications
4. High voltage levels cannot be High voltage levels can be
produced produced
5. High dv/dt and EMI Low dv/dt and EMI
6. High switching frequency, so Low switching frequency, so reduced
increased switching losses switching losses
5. Lower switching losses
6. Better electromagnetic compatibility
7. Higher power quality
Fig. 4.2 shows the classification of multilevel inverter topologies according to their
uses in power conversions.
A patent search carried out for more than 25 years show that multilevel inverter
circuits have been around since then. In 1975, an early traceable patent was cited
in which the cascade inverter was first stated with a format that comprises of sepa-
rately DC-sourced full-bridge cells in series to obtain a staircase shaped AC output
waveform voltage [4]. Through the investigation of the cascade inverter, with diodes
blocking the sources, the diode-clamped multilevel inverter was thereafter obtained.
The diode-clamped inverter was also called the neutral-point clamped (NPC) inverter
when it was first used in a three-level inverter in which the mid-voltage level was
defined as the neutral point. The NPC inverter effectively doubles the device voltage
level without requiring precise voltage matching; the circuit topology prevailed in the
1980s. The application of the NPC inverter and its extension to multilevel converter
was found in. Although the cascade inverter was invented earlier, its applications did
not prevail until the mid-1990s. Due to the great demand of medium-voltage high-
power inverters, the cascade inverter has drawn tremendous interest ever since [5].
Several patents were found for the use of cascade inverters in regenerative-type motor
drive applications.
2 Multilevel inverter topologies
2.1 Diode-clamped inverter
In 1981, the diode clamped (neutral point clamped) NPC multilevel inverter was intro-
duced by Nabae, Akagiand Takahashi, which was basically a three level neutral point