Page 122 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 122
HYDC03 12/5/05 5:37 PM Page 105
Chemical hydrogeology 105
BO X
Continued
3.7
(Type S2) located in areas of the aquifer with low hydraulic gradi- Mersey Valley area are very similar to Type 4, except it has a high
+
−
−
ents. The effects of modern groundwater abstractions are reflected Na /Cl equivalents ratios (Table 2) and a range of Cl concentra-
−1
by saline intrusion (Type S1) and recently induced recharge through tions from <10 to 1000 mg L . In both areas the saline–water
the Quaternary deposits (Type 2). interface is at a high level and groundwater flow rates are low. The
Example analyses of water Types 4 and 5 are shown in Table 2. hydrochemistry of Type 5 water is interpreted as having experienced
+
Type 5 water that occurs in the eastern confined areas and in the Na release by cation exchange following invasion by Type 4 water
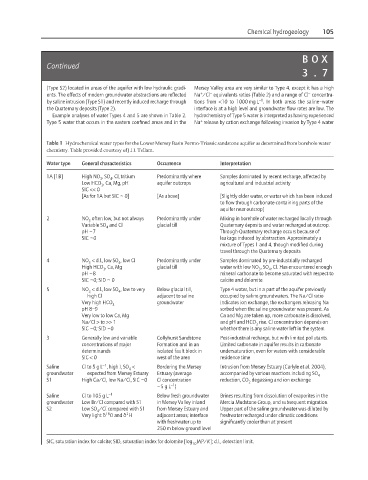
Table 1 Hydrochemical water types for the Lower Mersey Basin Permo-Triassic sandstone aquifer as determined from borehole water
chemistry. Table provided courtesy of J.H. Tellam.
Water type General characteristics Occurrence Interpretation
1A [1B] High NO , SO , Cl, tritium Predominantly where Samples dominated by recent recharge, affected by
3
4
Low HCO , Ca, Mg, pH aquifer outcrops agricultural and industrial activity
3
SIC << 0
[As for 1A but SIC ~ 0] [As above] [Slightly older water, or water which has been induced
to flow through carbonate-containing parts of the
aquifer near outcrop]
2 NO often low, but not always Predominantly under Mixing in borehole of water recharged locally through
3
Variable SO and Cl glacial till Quaternary deposits and water recharged at outcrop.
4
pH 7 Through-Quaternary recharge occurs because of
~
SIC 0 leakage induced by abstraction. Approximately a
~
mixture of Types 1 and 4, though modified during
travel through the Quaternary deposits
4 NO < d.l., low SO , low Cl Predominantly under Samples dominated by pre-industrially recharged
3
4
High HCO , Ca, Mg glacial till water with low NO , SO , Cl. Has encountered enough
3 3 4
pH 8 mineral carbonate to become saturated with respect to
~
SIC 0; SID ~ 0 calcite and dolomite
~
5 NO < d.l., low SO , low to very Below glacial till, Type 4 water, but in a part of the aquifer previously
4
3
high Cl adjacent to saline occupied by saline groundwaters. The Na/Cl ratio
Very high HCO 3 groundwater indicates ion exchange, the exchangers releasing Na
pH 8–9 sorbed when the saline groundwater was present. As
Very low to low Ca, Mg Ca and Mg are taken up, more carbonate is dissolved,
Na/Cl > to >> 1 and pH and HCO rise. Cl concentration depends on
3
SIC 0; SID 0 whether there is any saline water left in the system
~
~
3 Generally low and variable Collyhurst Sandstone Post-industrial recharge, but with limited pollutants.
concentrations of major Formation and in an Limited carbonate in aquifer results in carbonate
determinands isolated fault block in undersaturation, even for waters with considerable
SIC < 0 west of the area residence time
−1
Saline Cl to 5 g L , high I, SO < Bordering the Mersey Intrusion from Mersey Estuary (Carlyle et al. 2004),
4
groundwater expected from Mersey Estuary Estuary (average accompanied by various reactions including SO 4
S1 High Ca/Cl, low Na/Cl, SIC 0 Cl concentration reduction, CO degassing and ion exchange
~
2
−1
~ 5gL )
Saline Cl to 105 g L −1 Below fresh groundwater Brines resulting from dissolution of evaporites in the
groundwater Low Br/Cl compared with S1 in Mersey Valley inland Mercia Mudstone Group, and subsequent migration.
S2 Low SO /Cl compared with S1 from Mersey Estuary and Upper part of the saline groundwater was diluted by
4
18
2
Very light d O and d H adjacent areas; interface freshwater recharged under climatic conditions
with freshwater up to significantly cooler than at present
250 m below ground level
SIC, saturation index for calcite; SID, saturation index for dolomite [log IAP/K]; d.l., detection limit.
10