Page 120 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 120
HYDC03 12/5/05 5:36 PM Page 103
Chemical hydrogeology 103
Table 3.7 Surface area and cation exchange capacity (CEC) values to occur to restore carbonate equilibrium. However,
2+ 2+ 2+ 2+
for clays and Fe and Al oxyhydroxides. After Talibudeen (1981) once the Ca /Sr and Ca /Mg equivalents ratios
and Drever (1988).
fall below a certain critical level (~20 : 1 and 1 : 1,
respectively) cation exchange reactions become dom-
Surface area CEC 2+ 2+
2
−1
−1
(m g ) (meq 100 g ) inant and both Sr and Mg concentrations begin to
decrease (Edmunds & Walton 1983).
Fe and Al oxy-hydroxides 25–42 0.5–1 Cation exchange reactions are a feature of saline
(pH 8.0) water intrusion in coastal areas. Freshwater in coastal
~
Smectite 750–800 60–150 2+ −
3
Vermiculite 750–800 120–200 areas is typically dominated by Ca and HCO ions
Bentonite 750 100 from the dissolution of calcite such that cation
Illite 90–130 10–40 exchangers present in the aquifer have mostly Ca 2+
+
Kaolinite 10–20 1–10 adsorbed on their surfaces. In seawater, Na and Cl −
Chlorite – <10
are the dominant ions and aquifer materials in con-
+
tact with seawater will have Na attached to the
exchange surfaces. When seawater intrudes a coastal
freshwater aquifer, the following cation exchange
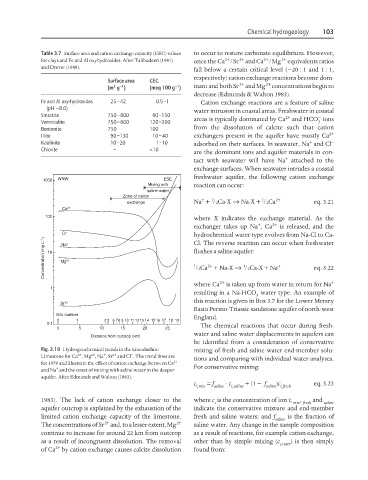
1000 WNW ESE
Mixing with reaction can occur:
saline water
Zone of cation + 2+
1
1
exchange Na + /2Ca-X → Na-X + /2Ca eq. 3.21
Ca 2+
100
where X indicates the exchange material. As the
+ 2+
exchanger takes up Na , Ca is released, and the
Cl − + hydrochemical water type evolves from Na-Cl to Ca-
Concentration (mg L −1 ) 10 Mg 2+ flushes a saline aquifer: + eq. 3.22
Cl. The reverse reaction can occur when freshwater
Na
2+
1
1
/2Ca + Na-X → /2Ca-X + Na
2+
where Ca is taken up from water in return for Na +
1
resulting in a Na-HCO water type. An example of
3
this reaction is given in Box 3.7 for the Lower Mersey
Sr 2+
Basin Permo-Triassic sandstone aquifer of north-west
Site number England.
0 1 2 3 6 78 9 10 11 1213 14 15 16 17 18 19
0.1 The chemical reactions that occur during fresh-
0 5 10 15 20 25
water and saline water displacements in aquifers can
Distance from outcrop (km)
be identified from a consideration of conservative
Fig. 3.19 Hydrogeochemical trends in the Lincolnshire mixing of fresh and saline water end-member solu-
2+ 2+ + 2+ −
Limestone for Ca , Mg , Na , Sr and Cl . The trend lines are
2+ tions and comparing with individual water analyses.
for 1979 and illustrate the effect of cation exchange between Ca
+ For conservative mixing:
and Na and the onset of mixing with saline water in the deeper
aquifer. After Edmunds and Walton (1983).
c = f · c + (1 − f )c eq. 3.23
i,mix saline i,saline saline i,fresh
1983). The lack of cation exchange closer to the where c is the concentration of ion i; , and
i mix fresh saline
aquifer outcrop is explained by the exhaustion of the indicate the conservative mixture and end-member
limited cation exchange capacity of the limestone. fresh and saline waters; and f saline is the fraction of
2+ 2+
The concentrations of Sr and, to a lesser extent, Mg saline water. Any change in the sample composition
continue to increase for around 22 km from outcrop as a result of reactions, for example cation exchange,
as a result of incongruent dissolution. The removal other than by simple mixing (c i,react ) is then simply
2+
of Ca by cation exchange causes calcite dissolution found from: