Page 132 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 132
Static controls and braking of motors 6/113
as fully controllable power switches, where they are
Y" P" required to handle only low powers. The latest trend is
to use them only as control devices.
The power BJTs and power MOSFETs have provided
two very useful static switching devices in the field of
transistor technology. But while the former can handle
larger powers, they dissipate high heat. the latter poses a
limitation in handling large powers. As a result of these
A npn A PnP
junction junction shortcomings, they are used mostly as control circuit
Circuit symbols switching devices. Such limitations were overcome by
yet another development in the 1990s, in the form of an
IGHT.
PC PC
Znszilated gate hipolar transistors (ZGBTs)
These are unidirectional transistors and have an insulated
gate (G) instead of the base (R) as in a bipolar transistor
Nectrical representation (RJT) and are represented in Figure 6.18. They are a
6 base hybrid combination of a przp bipolar transistor which is
E emitter connected to a power MOSFET like a two-junction
C collector transistor (power Darlington, Figure 6.16). A positive
(Note A diode has only one pn junction) voltage between the gate and the emitter switches ON
the MOSFET and provides a low resistance effect between
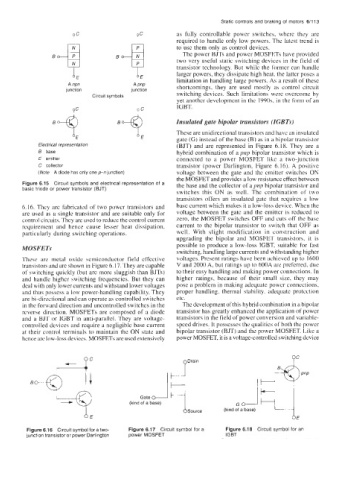
Figure 6.15 Circuit symbols and electrical representation of a the base and the collector of a pnp bipolar transistor and
basic triode or power transistor (BJT)
switches this ON as well. The combination of two
transistors offers an insulated gate that requires a low
6.16. They are fabricated of two power transistors and base current which makes it a low-loss device. When the
are used as a single transistor and are suitable only for voltage between the gate and the emitter is reduced to
control circuits. They are used to reduce the control current zero, the MOSFET switches OFF and cuts off the base
requirement and hence cause lesser heat dissipation, current to the bipolar transistor to switch that OFF as
particularly during switching operations. well. With slight modification in construction and
upgrading the bipolar and MOSFET transistors. it is
MOSFETs possible to produce a low-loss IGBT. suitable for fast
switching, handling large currents and withstanding higher
These are metal oxide semiconductor field effective voltages. Present ratings have been achieved up to 1600
transistors and are shown in Figure 6.17. They are capable V and 2000 A, but ratings up to 600A are preferred. due
of switching quickly (but are more sluggish than BJTs) to their easy handling and making power connections. In
and handle higher switching frequencies. But they can higher ratings, because of their small size, they may
deal with only lower currents and withstand lower voltages pose a problem in making adequate power connections.
and thus possess a low power-handling capability. They proper handling, thermal stability, adequate protection
are bi-directional and can operate as controlled switches etc.
in the forward direction and uncontrolled switches in the The development of this hybrid combination in a bipolar
reverse direction. MOSFE'Ts are composed of a diode transistor has greatly enhanced the application of power
and a BJT or IGBT in anti-parallel. They are voltage- transistors in the field of power conversion and variable-
controlled devices and require a negligible base current speed drives. It possesses the qualities of both the power
at their control terminals to maintain the ON state and bipolar transistor (RJT) and the power MOSFET. Like a
hence are low-loss devices. MOSFETs are used extensively power MOSFET, it is a voltage-controlled switching device
P"
ODrain
J
L
(kind of a base)
'a Source
Figure 6.16 Circuit symbol for a two- Figure 6.17 Circuit symbol for a Figure 6.18 Circuit symbol for an
junction transistor or power Darlington power MOSFET IGBT