Page 129 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 129
Speed control loop -
6/11 0 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
I I Torque control loop AC supply
I
.-
c
c
PID - proportional integral
derivative (a type of programming)
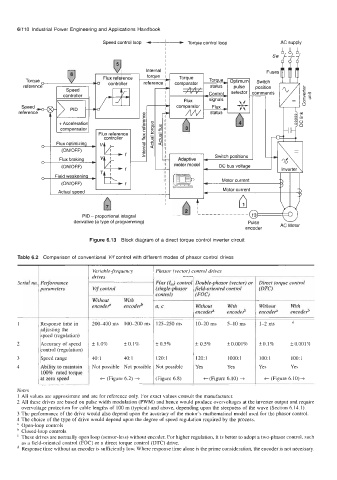
Figure 6.13 Block diagram of a direct torque control inverter circuit
Table 6.2 Comparison of conventional V/f control with different modes of phasor control drives
Variable-frequency Phasor (vector) control drives
drives
Serial no Performance Flux (I,,,) control Double-phasor (vector) or Direct torque control
parameters V/f control (single-phasor field-oriented control (DTC)
control) (FW
Without With
encode? encode# a, c Without With Without With
encode? encoderb encode? encode#
Response time in 200-400 ms 100-200 ms 125-250 ms 10-20 ms 5-10 ms 1-2 ms d
adjusting the
speed (regulation)
Accuracy of speed * 1.0% * 0.1% f 0.5% f 0.5% +0.001% *0.1% +0.001%
control (regulation)
Speed range 40: 1 40: 1 120:l 120:l 1000: 1 100: 1 1001
Ability to maintain Not possible Not possible Not possible Yes Yes Yes Yes
100% rated torque
at zero speed t (Figure 6.2) + (Figure 6.8) +(Figure 6.10) + t (Figure 6.10)+
Notes
1 All values are approximate and are for reference only. For exact values consult the manufacturer.
2 All these drives are based on pulse width modulation (PWM) and hence would produce overvoltages at the inverter output and require
overvoltage protection for cable lengths of 100 m (typical) and above, depending upon the steepness of the wave (Section 6.14.1).
3 The performance of the drive would also depend upon the accuracy of the motor’s mathematical model used for the phasor control.
4 The choice of the type of drive would depend upon the degree of speed regulation required by the process.
a Open-loop controls
Closed-loop controls
These drives are normally open loop (sensor-less) without encoder. For higher regulation, it is better to adopt a two-phasor control, such
as a field-oriented control (FOC) or a direct torque control (DTC) drive.
Response time without an encoder is sufficiently low. Where response time alone is the prime consideration, the encoder is not necessary.