Page 393 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 393
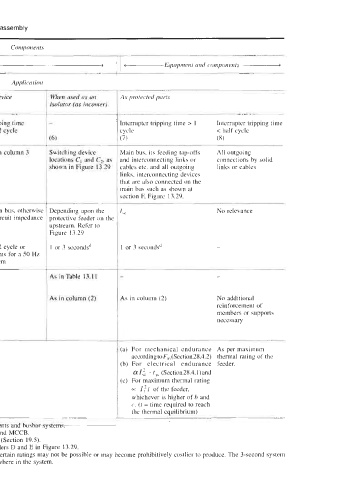
Components
< Interrupting devices > 1 -Equipment and components A
Application
When used as a protective device When used as a protected device When used as an As protected parts
(as incomer) 'as outgoing)' isolator (as incomer)
Parameters Tripping time Tripping time Tripping time Tripping time Interrupter tripping time > 1 Interrupter tripping time
> 1 cycle < half cycle > 1 cycle < 1/2 cycle cycle < half cycle
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (7) (8)
Type of devices OCBs", ACBs, MCCBs, As in column 2 As in column 3 Switching device Main bus, its feeding tap-offs All outgoing
MCCBs in LT and MCBs in LT and HRC locations C, and Cz, as and interconnecting links or connections by solid
MOCBS~ fuses in both LT Fhown in Figure 13.29 cables etc. and all outgoing links or cables
ABCBsb, SF, and and HT links, interconnecting devices
VCBs in HT that are also connected on the
main bus such as shown at
section F, Figure 13.29.
1, Short-time rating I,,, if connected on the main bus, otherwise Depending upon the No relevance
or symmetrical < Isc depending upon the circuit impedance protective feeder on the
fault level I,, upstream. Refer to
Figure 13.29
2 Duration of fault 1 or 3 secondsd <half cycle or 1 or 3 secondsd < 1/2 cycle or I or 3 secondsd 1 or 3 secondsd -
< 5 ms for a < 5 ms for a 50 Hz
t5'
50 Hz system system
I-
-
3 Making capacity I, As in Table 13.1 I As in Table 13. I1 As in Table 13.1 1
-
4 Endurance of According to As in column (2) - As in column (2) As in column (2) No additional
supporting and electrodynamic forces, reinforcement of
mounting structure, F,, = I; equation members or supports
load-bearing necessary
members and (28.4)
hardware
5 Cross-sectional area Taken care of by the manufacturer of the devices (a) For mechanical endurance As per maximum
of current-carrying a~cordingtoF~(Section28.4.2) thermal rating of the
metallic links or (b) For electrical endurance feeder.
cables ~rl: I,, (Section28.4.l)and
(c) For maximum thermal rating
= I:t of the feeder,
whichever is higher of b and
c. (I = time required to reach
the thermal eauilibrium)
Figure 13.29 illustrates a typical power distribution scheme to assign ratings to the various devices, components and husbar systems.
Wse of these breakers is gradually waning in the light of more advanced technologies available in an ACB and MCCB.
bUse of these breakers is also waning in the light of more advanced technologies available in SF, and VCBs (Section 19.5).
'These protect the circuits in the lower stream and are protected by a device in the upper stream such as feeders D and E in Figure 13.29.
dNormally only a I-second system is in use. The 3-second system is severe, for which protective devices in certain ratings may not be possible or may become prohibitively costlier to produce. The 3-second system
may, however, be used for a generator circuit to protect the generating source from a fallout on a fault elsewhere in the system.