Page 610 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 610
Voltage surges-causes, effects and remedies 17/575
OCB (MOCB or LOCB): Entrance coil
(suitable for a
5 kV + 5.4 kV = 10.4 kV BIL of (3p.u.16))
-~
[l P.U. = 12
x 6.6 = 5.4 kV
SF, breaker: 7.5 kV + 5.4 kV = 12.9 kV
Vacuum breaker with copper-chromium contacts:
6 kV + 5.4 kV = 11.4 kV
Vacuum breaker with copper-bismuth contacts:
35 kV + 5.4 kV = 40.4 kV.
From the above it can be noted that the surge voltages -Jy vl= 3p. .
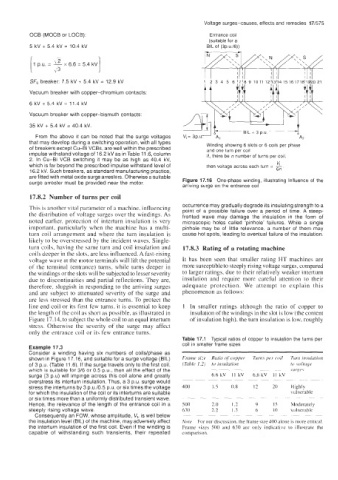
that may develop during a switching operation, with all types Winding showing 6 slots or 6 coils per phase
of breakers except Cu-Bi VCBs, are well within the prescribed and one turn per coil
impulse withstand voltage of 16.2 kV as in Table 11.6, column If, there be n number of turns per coil.
2. In Cu-Bi VCB switching it may be as high as 40.4 kV,
Vt
which is far beyond the prescribed impulse withstand level of then voltage across each turn = -
16.2 kV. Such breakers, as standard manufacturing practice, 6n
are fitted with metal oxide surge arresters. Otherwise a suitable Figure 17.16 One-phase winding, illustrating Influence of the
surge arrester must be provided near the motor.
arriving surge on the entrance coil
17.8.2 Number of turns per coil
This is another vital parameter of a machine, influencing occurrence may gradually degrade its insulating strength to a
point of a possible failure over a period of time. A steep-
the distribution of voltage surges over the windings. As fronted wave may damage the insulation in the form of
noted earlier, protection of interturn insulation is very microscopic holes called 'pinhole' failures. While a single
important, particularly when the machine has a multi- pinhole may be of little relevance, a number of them may
turn coil arrangement and where the turn insulation is cause hot spots, leading to eventual failure of the insulation.
likely to be overstressed by the incident waves. Single-
turn coils. having the same turn and coil insulation and 17.8.3 Rating of a rotating machine
coils deeper in the slots, are less influenced. A fast-rising
voltage wave at the motor terminals will lift the potential It has been seen that smaller rating HT machines are
of the terminal (entrance) turns, while turns deeper in more susceptible to steeply rising voltage surges, compared
the windings or the slots will be subjected to lesser severity to larger ratings, due to their relatively weaker interturn
due to discontinuities and partial reflections. They are, insulation and require more careful attention to their
therefore, sluggish in responding to the arriving surges adequate protection. We attempt to explain this
and are subject to attenuated severity of the surge and phenomenon as follows:
are less stressed than the entrance turns. To protect the
line end coil or its first few turns. it is essential to keep 1 In smaller ratings although the ratio of copper to
the length of the coil as short as possible, as illustrated in insulation of the windings in the slot is low (the content
Figure 17.14, to subject the whole coil to an equal interturn of insulation high), the turn insulation is low, roughly
stress. Otherwise the severity of the surge may affect
only the entrance coil or its few entrance turns.
Table 17.1 Typical ratios of copper to insulation the turns per
coil in smaller frame sizes
Example 17.3
Consider a winding having six numbers of coilslphase as ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~~~ ~ ~ ~ ~
shown in Figure 17.16, and suitable for a surge voltage (BIL) Frame size Ratio of copper Turns per- coil Turn rnsulation
of 3 p.u. (Table 11.6). If the surge travels only to the first coil, (Table 1.2) to insularion to wlrclge
which is suitable for 3/6 or 0.5 P.u., then all the effect of the ~- ~~ srtrgcs
6.6 kV 11 kV
6.6 kV II kV
surge (3 p.u) will impinge across this coil alone and greatly -~ - - ~- -~
overstress its interturn insulation. Thus, a 3 p.u. surge would ~ ~ ~ ~~~
stress the interturns by 3 p.u./0.5 p.u. or six times the voltage 400 1.5 0.8 12 20 Highly
for which the insulation of the coil or its interturns are suitable vulnerable
or six times more than a uniformly distributed transient wave. ~ - -~ - - -~ ~~ ~~ ~~~~ ~~ ~~~ ~~
Hence, the relevance of the length of the entrance coil in a 5 00 2.0 1.2 9 15 Moderately
steeply rising voltage wave. 630 2.2 1.3 6 IO vulnerable
Consequently an FOW, whose amplitude, V,, is well below ~~~ ~ - ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~~ ~ ~-
~
the insulation level (BIL) of the machine, may adversely affect Note For our discussion, the frame size 400 alone is more critical.
the interturn insulation of the first coil. Even if the winding is Frame sizes 500 and 630 are only indicative to illustrate the
capable of withstanding such transients, their repeated comparison.