Page 672 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 672
Circuit interrupters 19/637
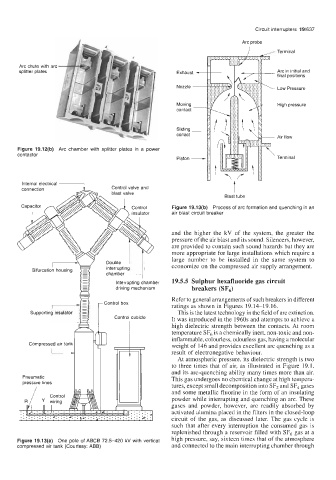
Arc probe
,/ Terminal
Arc chute with arc
splitter plates Arc in initial and
final positions
Low Pressure
High pressure
Air flow
Figure 19.12(b) Arc chamber with splitter plates in a power
contactor Piston - Terminal
Internal electrical t
connection Control valve and
blast valve
Blast tube
Control Figure 19.13(b) Process of arc formation and quenching in an
insulator air blast circuit breaker
and the higher the kV of the system, the greater the
pressure of the air blast and its sound. Silencers, however,
are provided to contain such sound hazards but they are
more appropriate for large installations which require a
Double A large number to be installed in the same system to
interrupting economize on the compressed air supply arrangement.
chamber
Interrupting chamber 19.5.5 Sulphur hexafluoride gas circuit
driving mechanism breakers (SF,)
Refer to general arrangements of such breakers in different
ratings as shown in Figures 19.14-19.16.
This is the latest technology in the field of arc extinction.
It was introduced in the 1960s and attempts to achieve a
high dielectric strength between the contacts. At room
temperature SF6 is a chemically inert, non-toxic and non-
inflammable, colourless, odourless gas, having a molecular
Compressed air tank weight of 146 and provides excellent arc quenching as a
result of electronegative behaviour.
At atmospheric pressure, its dielectric strength is two
to three times that of air, as illustrated in Figure 19.1,
and its arc-quenching ability many times more than air.
Pneumatic This gas undergoes no chemical change at high tempera-
tures, except small decomposition into SF2 and SF, gases
and some metallic fluorine in the form of an insulating
powder while interrupting and quenching an arc. These
gases and powder, however, are readily absorbed by
activated alumina placed in the filters in the closed-loop
circuit of the gas, as discussed later. The gas cycle is
such that after every interruption the consumed gas is
replenished through a reservoir filled with SF6 gas at a
Figure 19.13(a) One pole of ABCB 72.5-420 kV with vertical high pressure, say, sixteen times that of the atmosphere
compressed air tank (Courtesy: ABB) and connected to the main interrupting chamber through