Page 70 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 70
Duties of induction motors 3/51
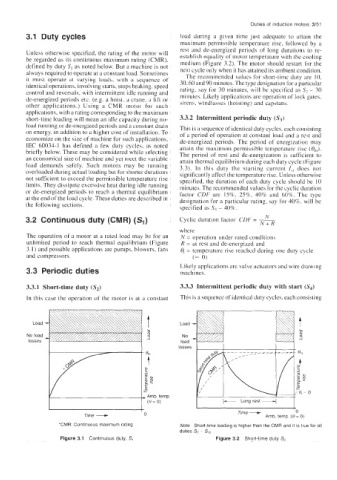
3.1 Duty cycles load during a given time just adequate to attain the
maximum permissible temperature rise, followed by a
Unless otherwise specified, the rating of the motor will rest and de-energized periods of long durations to re-
be regarded as its continuous maximum rating (CMR), establish equality of motor temperature with the cooling
defined by duty S, as noted below. But a machine is not medium (Figure 3.2). The motor should restart for the
next cycle only when it has attained its ambient condition.
always required to operate at a constant load. Sometimes The recommended values for short-time duty are 10,
it must operate at varying loads, with a sequeiice of 30,60 and 90 minutes. The type designation for a particular
identical operations, involving starts, stops braking, speed
control and reversals, with intermittent idle running and rating, say for 30 minutes, will be specified as S1_ - 30
de-energized periods etc. (e.g. a hoist, a crane, a lift or minutes. Likely applications are operation of lock gates,
other applications.) Using a CMR motor for such sirens, windlasses (hoisting) and capstans.
applications, with a rating corresponding to the maximum
short-time loading will mean an idle capacity during no- 3.3.2 Intermittent periodic duty (S,)
load running or de-energized periods and a constant drain This is a sequence of identical duty cycles. each consisting
on energy. in addition to a higher cost of installation. To of a period of operation at constant load and a rest and
economize on the size of machine for such applications, de-energized periods. The period of energization may
IEC 60034-1 has defined a few duty cycles, as noted attain the maximum permissible temperature rise (On,).
briefly below. These may be considered while selecting The period of rest and de-energization is sufficient to
an economical size of machine and yet meet the variable attain thermal equilibrium during each duty cycle (Figure
load demands safely. Such motors may be running 3.3). In this duty the starting current I,, does not
overloaded during actual loading but for shorter durations significantly affect the temperature rise. Unless otherwise
not sufficient to exceed the permissible temperature rise specified, the duration of each duty cycle should be IO
limits. They dissipate excessive heat during idle running minutes. The recommended values for the cyclic duration
or de-energized periods to reach a thermal equilibrium factor CDF are IS%, 2596, 40% and 60%. The type
at the end of the load cycle. These duties are described in designation for a particular rating, say for 40%. will be
the following sections. specified as S3 - 40%.
N
3.2 Continuous duty (CMR) (SI) Cyclic duration factor CDF = ~ N+R
where
The operation of a motor at a rated load may be for an N = operation under rated conditions
unlimited period to reach thermal equilibrium (Figure R = at rest and de-energized and
3.1) and possible applications are pumps, blowers, fans 0, = temperature rise reached during one duty cycle
and compressors. (= 0)
Likely applications are valve actuators and wire drawing
3.3 Periodic duties machines.
3.3.1 Short-time duty (S,) 3.3.3 Intermittent periodic duty with start (S,)
In this case the operation of the motor is at a constant This is a sequence of identical duty cycles. each consisting
1
Load f
2
No loaa .... No
losscs load 4
a
E
I L V A m temp
(H= 0) b
T,me -
Time - 0 (H= 0) + Long rest+ '0
,Amb
temp
Amb temp (0 = 0)
*CMR: Continuous maximum rating Note Short-time loading IS higher than the CMR and it is true for all
duties S2 - S,,
Figure 3.1 Continuous duty, S, Figure 3.2 Short-time duty S,