Page 74 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 74
Duties of induction motors 3/55
We have considered three different speeds (lower Nr, D = period of starting
to higher Nr3) for this duty cycle, having three CDFs for N1, N2, Ni = operations within rated load (PI)
one cycle, each corresponding to a different speed. N4 = operation during overload (P2)
For this duty type, the abbreviation is followed by the F = changeover of speed by electrical braking
indication of the number of duty cycles per hour, the FI R = at rest and de-energized,
and the load at the various speeds. 6, = temperature rise reached during one duty
As an illustration the CDF must be indicated for each cycle (= 0)
speed as follows:
3.3.9 Duty with discrete constant loads (Sl0)
c /I1 FI kW Speed CDF This is a type of duty consisting of a number of varying
(rp m ) % loads, not more than four in each cycle. Each load is
.
~~ ~ ~~ performed for sufficient duration to allow the machine
20 25 10 1440 60 to attain its thermal equilibrium (Figure 3.10). It is,
20 25 6 960 40
20 25 1 730 40 however, permitted that each load cycle may not be
-~ identical, provided that each discrete loading during one
~ ~~~
particular load cycle is performed for a sufficient duration
Likely applications are where the motor is required to to attain thermal equilibrium. The temperature attained
run at different speeds. during each discrete loading is within permissible limits
or within such limits that if it exceeds the permissible
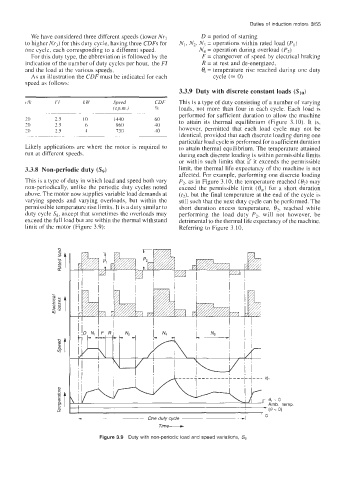
3.3.8 Non-periodic duty (S,) limit, the thermal life expectancy of the machine is not
affected. For example, performing one discrete loading
This is a type of duty in which load and speed both vary P2, as in Figure 3.10, the temperature reached (e2) may
non-periodically, unlike the periodic duty cycles noted exceed the permissible limit (en,) for a short duration
above. The motor now supplies variable load demands at (t2), but the final temperature at the end of the cycle is
varying speeds and varying overloads, but within the still such that the next duty cycle can be performed. The
permissible temperature rise limits. It is a duty similar to short duration excess temperature, €$, reached while
duty cycle S8, axcept that sometimes the overloads may performing the load duty P2, will not however, be
exceed the full load but are within the thermal withstand detrimental to the thermal life expectancy of the machine.
limit of the motor (Figure 3.9): Referring to Figure 3.10,
I i I I !
L L J 1 1
One duty cycle
~ ~
Tme-
Figure 3.9 Duty with non-periodic load and speed variations, S,