Page 71 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 71
3/52 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
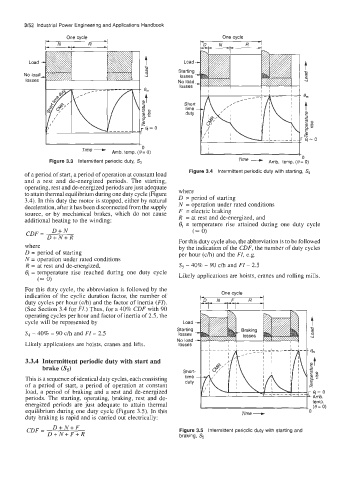
One cycle One cycle
P N R -I FD, N ,
t
Load t
rl
8
No load 4 -0
8
4
Time -
I I 0
Amb. temp. (e = 0) I 1 ' Time -
10
Figure 3.3 Intermittent periodic duty, S, Amb. temp. (e= 0)
Figure 3.4 Intermittent periodic duty with starting, S,
of a period of start, a period of operation at constant load
and a rest and de-energized periods. The starting,
operating, rest and de-energized periods are just adequate
to attain thermal equilibrium during one duty cycle (Figure where
3.4). In this duty the motor is stopped, either by natural D = period of starting
deceleration, after it has been disconnected from the supply N = operation under rated conditions
source, or by mechanical brakes, which do not cause F = electric braking
additional heating to the winding: R = at rest and de-energized, and
6, = temperature rise attained during one duty cycle
D+N (= 0)
CDF= D+N+R For this duty cycle also, the abbreviation is to be followed
where by the indication of the CDF, the number of duty cycles
D = period of starting per hour (c/h) and the FI, e.g.
N = operation under rated conditions
R = at rest and de-energized, S5 - 40% - YO c/h and FI - 2.5
6, = temperature rise reached during one duty cycle Likely applications are hoists, cranes and rolling mills.
(= 0)
For this duty cycle, the abbreviation is followed by the
indication of the cyclic duration factor, the number of One cycle
duty cycles per hour (CAI) and the factor of inertia (FZ). kM
(See Section 3.4 for FI.) Thus, for a 40% CDF with YO
operating cycles per hour and factor of inertia of 2.5, the
cycle will be represented by Load t
S4 - 40% - YO c/h and FI - 2.5 Starting 5
losses
4
No load
Likely applications are hoists, cranes and lifts. losses I ~ I 1 I 1 I 1
3.3.4 Intermittent periodic duty with start and
brake (S,)
This is a sequence of identical duty cycles, each consisting
of a period of start, a period of operation at constant
load, a period of braking and a rest and de-energized
periods. The starting, operating, braking, rest and de-
energized periods are just adequate to attain thermal Time - (e =
temp. 0)
equilibrium during one duty cycle (Figure 3.5). In this 0
duty braking is rapid and is carried out electrically:
D+N+F
CDF = Figure 3.5 Intermittent periodic duty with starting and
D+N+F+R braking, S,