Page 76 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 76
Duties of induction motors 3/57
-t
1
&
c
m
x
N
Heating ~-
&
x
m
(D
1
- T,me - Cooling --
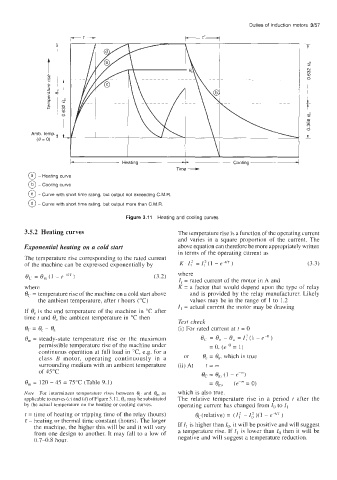
@ - Heating curve
@ - Cooling curve
@ - Curve with short time rating, but output not exceeding C.M.R
@ - Curve with short time rating, but output more than C.M.R.
Figure 3.1 1 Heating and cooling curves
3.5.2 Heating curves The temperature rise is a function of the operating current
and varies in a square proportion of the current. The
Exponential heating on a cold start above equation can therefore be more appropriately written
in terms of the operating current as
The temperature rise corresponding to the rated current
of the machine can be expressed exponentially by K.Z,? = I:(1 -e-'T) (3.3)
where
6, = 8, (1 - e-"Z ) (3.2)
I, = rated current of the motor in A and
where K = a factor that would depend upon the type of relay
6, = temperature rise of the machine on a cold start above and is provided by the relay manufacturer. Likely
the ambient temperature, after t hours ("C) values may be in the range of 1 to 1.2
I, = actual current the motor may be drawing
If 0, is the end temperature of the machine in "C after
time t and Ox the ambient temperature in "C then
Test check
6, = 6, ~ 6, (i) For rated current at t = 0
6, = steady-state temperature rise or the maximum Bc = 6, - 8, = Ir2 (1 - e-" )
permissible temperature rise of the machine under = 0, (e-" = 1)
continuous operation at full load in "C, e.g. for a
class B motor, operating continuously in a or 0, = e,, which is true
surrounding medium with an ambient temperature (ii) At t = m
of 45°C 0, = 8, (1 - C)
6, = 120 - 45 = 75°C (Table 9.1) = e,, (e? = 0)
Note For intermittent temperature rises between 0, and e,, as which is also true.
applicable to curves (c) and (d) of Figure 3.1 1, e,, may be substituted The relative temperature rise in a period t after the
by the actual temperature on the heating or cooling curves. operating current has changed from Io to I,
t = time of heating or tripping time of the relay (hours) Oc(re1ative) = (I: - I: )(I -
t = heating or thermal time constant (hours). The larger
the machine, the higher this will be and it will vary If I, is higher than Io, it will be positive and will suggest
from one design to another. It may fall to a low of a temperature rise. If I, is lower than I,, then it will be
0.7-0.8 hour. negative and will suggest a temperature reduction.