Page 910 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 910
Carrying power through metal-enclosed bus systems 28/861
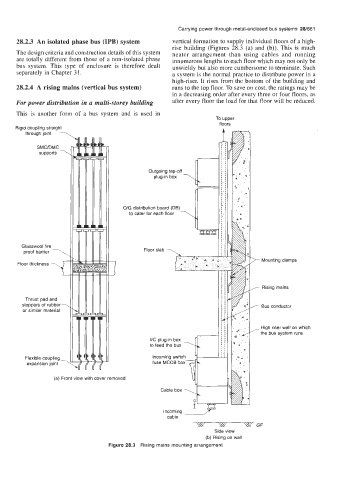
28.2.3 An isolated phase bus (IPB) system vertical formation to supply individual floors of a high-
rise building (Figures 28.3 (a) and (b)). This is much
The design criteria and construction details of this system neater arrangement than using cables and running
are totally different from those of a non-isolated phase innumerous lengths to each floor which may not only be
bus system. This type of enclosure is therefore dealt unwieldy but also more cumbersome to terminate. Such
separately in Chapter 3 1. a system is the normal practice to distribute power in a
high-riser. It rises from the bottom of the building and
28.2.4 A rising mains (vertical bus system) runs to the top floor. To save on cost, the ratings may be
in a decreasing order after every three or four floors, as
For power distribution in a multi-storey building after every floor the load for that floor will be reduced.
This is another form of a bus system and is used in
To upper
floors
Rigid coupling straight
-'f
supports -
through joint
SMC/DMC
rl
Outgoing tap-off
plug-in box
O/G distribution board (DB)
to cater for each floor
Glasswool fire Floor slab -,
proof barrier 1 i
Y I b *
Floor thickness Mounting clamps
Rising mains
stoppers of rubber - Bus conductor
Thrust pad and
or similar material
High riser wall on which
the bus system runs
I/C plug-in box
to feed the bus
Flexible coupling - Incoming switch
expansion joint fuse MCCB box d
(a) Front view with cover removed
Cable box
Incoming
cable
GF
Side view
(b) Rising on wall
Figure 28.3 Rising mains mounting arrangement