Page 97 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 97
4/78 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
Through semiconductor devices (static drives)
In a solid-state static switching device the voltage can be
varied smoothly to any required value from high to low
or low to high without creating a condition of open
transient. For HT motors particularly and large LT motors
generally, it provides a more recommended alternative
over an autotransformer or a YIA starting. For details see
Section 6.16.1.
Through static electrodes liquid electrolyte or
chemical resistance starting
This is a primary resistance starting and has a well-proven
French technology for soft starting of all types of induction
motors. The device works on the principle of a decrease
in resistance of an electrolyte (chemical) having a negative
temperature coefficient. The passing of the starting current
through the electrolyte raises its temperature inside a IO
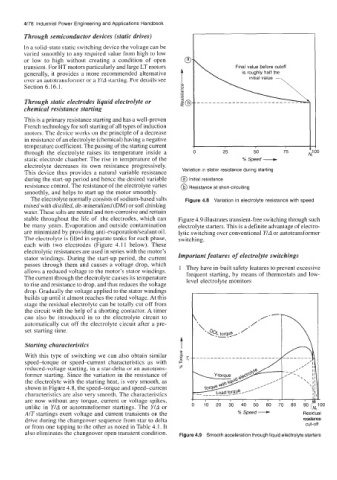
static electrode chamber. The rise in temperature of the % Speed ---+ , .1
electrolyte decreases its own resistance progressively.
This device thus provides a natural variable resistance Variation in stator resistance during starting
during the start-up period and hence the desired variable @ Initial resistance
resistance control. The resistance of the electrolyte varies (@ Resistance at short-circuiting
smoothly, and helps to start up the motor smoothly.
The electrolyte normally consists of sodium-based salts Figure 4.8 Variation in electrolyte resistance with speed
mixed with distilled, de-mineralized (DM) or soft drinking
water. These salts are neutral and non-corrosive and remain
stable throughout the life of the electrodes, which can Figure 4.9 illustrates transient-free switching through such
be many years. Evaporation and outside contamination electrolyte starters. This is a definite advantage of electro-
are minimized by providing anti-evaporationIsealant oil. lytic switching over conventional YlA or autotransformer
The electrolyte is filled in separate tanks for each phase, switching.
each with two electrodes (Figure 4.11 below). These
electrolytic resistances are used in series with the motor’s
stator windings. During the start-up period, the current Important features of electrolyte switchings
passes through them and causes a voltage drop, which 1 They have in-built safety features to prevent excessive
allows a reduced voltage to the motor’s stator windings. frequent starting, by means of thermostats and low-
The current through the electrolyte causes its temperature level electrolyte monitors
to rise and resistance to drop, and thus reduces the voltage
drop. Gradually the voltage applied to the stator windings
builds up until it almost reaches the rated voltage. At this
stage the residual electrolyte can be totally cut off from
the circuit with the help of a shorting contactor. A timer
can also be introduced in to the electrolyte circuit to
automatically cut off the electrolyte circuit after a pre-
set starting time.
Starting characteristics
With this type of switching we can also obtain similar
speed-torque or speed-current characteristics as with
reduced-voltage starting, in a star-delta or an autotrans-
former starting. Since the variation in the resistance of
the electrolyte with the starting heat, is very smooth, as
shown in Figure 4.8, the speed-torque and speed-current
characteristics are also very smooth. The characteristics
are now without any torque, current or voltage spikes, % Speed -
unlike in YIA or autotransformer startings. The YIA or 00
AIT startings exert voltage and current transients on the Residual
drive during the changeover sequence from star to delta
or from one tapping to the other as noted in Table 4.1. It cut-off
also eliminates the changeover open transient condition. Figure 4.9 Smooth acceleration through liquid electrolyte starters