Page 284 - Industrial Process Plant Construction Estimating and Man Hour Analysis
P. 284
Statistical applications to construction Chapter 12 263
12.9.4 Contingency
Contingency is a cost element that makes allowance for the unknown risk asso-
ciated with a project. Contingency cost estimates are assembled when minimum
information is provided in the bid documents and where prior experience and
data are lacking. Projects requiring excessive research, development, and
design are the best candidates for contingency.
Contingency cost estimating is an application of the range method. Three
values for each construction task, lowest, L; most likely, M; and the highest,
H, are estimated. Values of the upper limit, UL, are estimated and cover the
potential range of overrun or underrun of the project. Estimate values depend
on the risk involved in construction.
12.9.5 Application of the range method to contingency
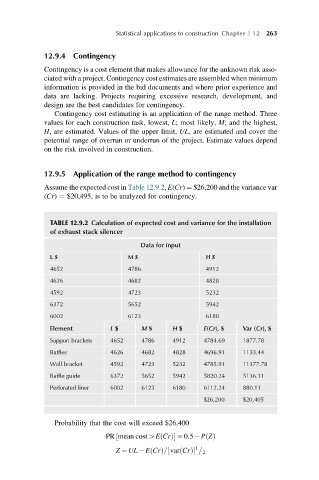
Assume the expected cost in Table 12.9.2, E(Cr) ¼ $26,200 and the variance var
(Cr) ¼ $20,495, is to be analyzed for contingency.
TABLE 12.9.2 Calculation of expected cost and variance for the installation
of exhaust stack silencer
Data for input
L $ M $ H $
4652 4786 4912
4626 4682 4828
4592 4723 5232
6372 5652 5942
6002 6123 6180
Element L $ M $ H $ E(Cr), $ Var (Cr), $
Support brackets 4652 4786 4912 4784.69 1877.78
Baffles 4626 4682 4828 4696.91 1133.44
Wall bracket 4592 4723 5232 4785.91 11377.78
Baffle guide 6372 5652 5942 5820.24 5136.11
Perforated liner 6002 6123 6180 6112.24 880.11
$26,200 $20,405
Probability that the cost will exceed $26,400
ð
½
PR mean cost > ECrÞ ¼ 0:5 PZðÞ
1
ð
Z ¼ UL ECrÞ= var CrÞ 2
ð
½