Page 445 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 445
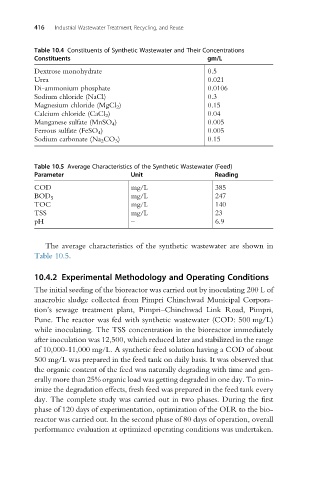
416 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
Table 10.4 Constituents of Synthetic Wastewater and Their Concentrations
Constituents gm/L
Dextrose monohydrate 0.5
Urea 0.021
Di-ammonium phosphate 0.0106
Sodium chloride (NaCl) 0.3
Magnesium chloride (MgCl 2 ) 0.15
Calcium chloride (CaCl 2 ) 0.04
Manganese sulfate (MnSO 4 ) 0.005
Ferrous sulfate (FeSO 4 ) 0.005
Sodium carbonate (Na 2 CO 3 ) 0.15
Table 10.5 Average Characteristics of the Synthetic Wastewater (Feed)
Parameter Unit Reading
COD mg/L 385
mg/L 247
BOD 5
TOC mg/L 140
TSS mg/L 23
pH – 6.9
The average characteristics of the synthetic wastewater are shown in
Table 10.5.
10.4.2 Experimental Methodology and Operating Conditions
The initial seeding of the bioreactor was carried out by inoculating 200 L of
anaerobic sludge collected from Pimpri Chinchwad Municipal Corpora-
tion’s sewage treatment plant, Pimpri–Chinchwad Link Road, Pimpri,
Pune. The reactor was fed with synthetic wastewater (COD: 500 mg/L)
while inoculating. The TSS concentration in the bioreactor immediately
after inoculation was 12,500, which reduced later and stabilized in the range
of 10,000-11,000 mg/L. A synthetic feed solution having a COD of about
500 mg/L was prepared in the feed tank on daily basis. It was observed that
the organic content of the feed was naturally degrading with time and gen-
erally more than 25% organic load was getting degraded in one day. To min-
imize the degradation effects, fresh feed was prepared in the feed tank every
day. The complete study was carried out in two phases. During the first
phase of 120 days of experimentation, optimization of the OLR to the bio-
reactor was carried out. In the second phase of 80 days of operation, overall
performance evaluation at optimized operating conditions was undertaken.