Page 560 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 560
530 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
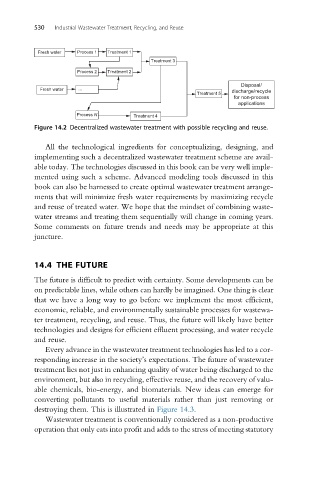
Fresh water Process 1 Treatment 1
Treatment 3
Process 2 Treatment 2
Disposal/
Fresh water ... discharge/recycle
Treatment 5
for non-process
applications
Process N Treatment 4
Figure 14.2 Decentralized wastewater treatment with possible recycling and reuse.
All the technological ingredients for conceptualizing, designing, and
implementing such a decentralized wastewater treatment scheme are avail-
able today. The technologies discussed in this book can be very well imple-
mented using such a scheme. Advanced modeling tools discussed in this
book can also be harnessed to create optimal wastewater treatment arrange-
ments that will minimize fresh water requirements by maximizing recycle
and reuse of treated water. We hope that the mindset of combining waste-
water streams and treating them sequentially will change in coming years.
Some comments on future trends and needs may be appropriate at this
juncture.
14.4 THE FUTURE
The future is difficult to predict with certainty. Some developments can be
on predictable lines, while others can hardly be imagined. One thing is clear
that we have a long way to go before we implement the most efficient,
economic, reliable, and environmentally sustainable processes for wastewa-
ter treatment, recycling, and reuse. Thus, the future will likely have better
technologies and designs for efficient effluent processing, and water recycle
and reuse.
Every advance in the wastewater treatment technologies has led to a cor-
responding increase in the society’s expectations. The future of wastewater
treatment lies not just in enhancing quality of water being discharged to the
environment, but also in recycling, effective reuse, and the recovery of valu-
able chemicals, bio-energy, and biomaterials. New ideas can emerge for
converting pollutants to useful materials rather than just removing or
destroying them. This is illustrated in Figure 14.3.
Wastewater treatment is conventionally considered as a non-productive
operation that only eats into profit and adds to the stress of meeting statutory