Page 299 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 299
Measurement techniques: radiation thermometers 283
particularly at high temperatures. The thermistor
bridge provides compensation for changes in the
sensitivity of the thermopile at high temperatures,
but if the head is too hot to touch it is in danger
of damage to soldered joints, insulation, etc.
The instrument may be used to measure the
mean emissivity of a surface for all wavelengths
up to about 10 pm. This value can be used for the
correction of total radiation thermometer read-
ings. A black hemispherical insert is provided
with the instrument which can be clipped into
the hemispherical reflector to cover the gold. If
two measurements are made, one with the gold
covered and the other with the gold exposed, the
emissivity can readily be deduced from the two
measurements. A graph provided with the instru-
ment enables the emissivity to be derived easily
from the two readings. while a second graph gives
an indication of the error involved in the tem-
perature measurement of the hot body.
Calibration of total rcrdiatiorz tlzernioineters A
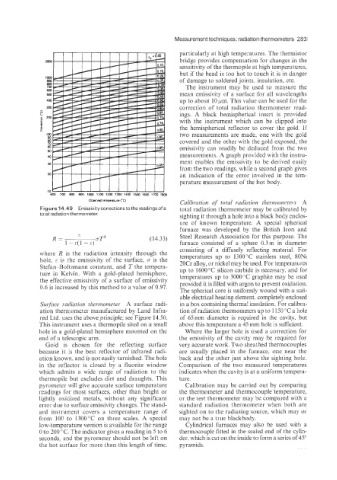
Figure 14.49 Emissivitycorrectionsto thereadingsofa total radiation thermometer may be calibrated by
total radiation thermometer. sighting it through a hole into a black body enclos-
ure of known temperature. A special spherical
furnace was developed by the British Iron and
i- Steel Research Association for this purpose. The
R= OT4 (14.33)
1 - r(l - E) furnace consisted of a sphere 0.3m in diameter
consisting of a diffusely reflecting material. For
where R is the radiation intensity through the temperatures up to 1300°C stainless steel, 80Ni
hole, E is the emissivity of the surface, o is the 20Cr alloy, or nickel may be used. For temperatures
Stefan-Boltzmann constant, and T the tempera- up to 1600°C silicon carbide is necessary, and for
ture in Kelvin. With a gold-plated hemisphere. temperatures up to 3000 "C graphite may be used
the effective emissivity of a surface of emissivity provided it is filled with argon to prevent oxidation.
0.6 is increased by this method to a value of 0.97.
The spherical core is uniformly wound with a suit-
able electrical heating element. completely enclosed
Stirjbce radic~tion therrnonzeter A surface radi- in a box containing thermal insulation. For calibra-
ation thermometer manufactured by Land Infra- tion of radiation thermometers up to 1150 "C a hole
red Ltd. uses the above principle; see Figure 14.50. of 65mm diameter is required in the cavity, but
This instrument uses a thermopile sited on a small above this temperature a 45 mm hole is sufficient.
hole in a gold-plated hemisphere mounted on the Where the larger hole is used a correction for
end of a telescopic arm. the emissivity of the cavity may be required for
Cold is chosen for the reflecting surface very accurate work. Two sheathed thermocouples
because it is the best reflector of infrared radi- are usually placed in the furnace. one near the
ation known, and is not easily tarnished. The hole back and the other just above the sighting hole.
in the reflector is closed by a fluorite window Comparison of the two measured temperatures
which admits a wide range of radiation to the indicates when the cavity is at a uniform tempera-
thermopile but excludes dirt and draughts. This ture.
pyrometer will give accurate surface temperature Calibration may be carried out by comparing
readings for most surfaces, other than bright or the thermometer and thermocouple temperature.
lightly oxidized metals, without any significant or the test thermometer may be compared with a
error due to surface emissivity changes. The stand- standard radiation thermometer when both are
ard instrument covers a temperature range of sighted on to the radiating source, which may or
from 100 to 1300°C on three scales. A special may not be a true blackbody.
low-temperature version is available for the range Cylindrical furnaces may also be used with a
0 to 100 "C. The indicator gives a reading in 5 to 6 thermocouple fitted in the sealed end of the cylin-
seconds, and the pyrometer should not be left on der. which is cut on the inside to form a series of45"
the hot surface for more than this length of time. pyramids.