Page 301 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 301
Measurement techniques: radiation thermometers 285
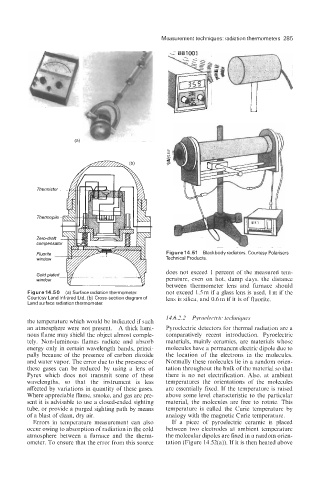
Figure 14.51 Blackbody radiators. Courtesy Polarisers
Technical Products.
does not exceed 1 percent of the measured tem-
perature, even on hot, damp days, the distance
between thermometer lens and furnace should
Figure 14.50 (a) Surface radiation thermometer. not exceed 1.5 m if a glass lens is used, 1 m if the
Courtesy Land Infrared Ltd. (b) Cross-section diagram of lens is silica, and 0.6 m if it is of fluorite.
Land surface radiation thermometer.
14.6.2.2 Pyroelectric techniques
the temperature which would be indicated if such
an atmosphere were not present. A thick lumi- Pyroelectric detectors for thermal radiation are a
nous flame may shield the object almost comple- comparatively recent introduction. Pyroelectric
tely. Non-luminous flames radiate and absorb materials, mainly ceramics, are materials whose
energy only in certain wavelength bands, princi- molecules have a permanent electric dipole due to
pally because of the presence of carbon dioxide the location of the electrons in the molecules.
and water vapor. The error due to the presence of Normally these molecules lie in a random orien-
these gases can be reduced by using a lens of tation throughout the bulk of the material so that
Pyrex which does not transmit some of these there is no net electrification. Also, at ambient
wavelengths, so that the instrument is less temperatures the orientations of the molecules
affected by variations in quantity of these gases. are essentially fixed. If the temperature is raised
Where appreciable flame, smoke, and gas are pre- above some level characteristic to the particular
sent it is advisable to use a closedended sighting material, the molecules are free to rotate. This
tube, or provide a purged sighting path by means temperature is called the Curie temperature by
of a blast of clean, dry air. analogy with the magnetic Curie temperature.
Errors in temperature measurement can also If a piece of pyroelectric ceramic is placed
occur owing to absorption of radiation in the cold between two electrodes at ambient temperature
atmosphere between a furnace and the therm- the molecular dipoles are fixed in a random orien-
ometer. To ensure that the error from this source tation (Figure 14.52(a)). If it is then heated above