Page 302 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 302
286 Temperature measurement
P resulting external electric field is a coilstant C
which is a function of the material. If the field
due to the applied voltage was E and the polar-
ization P then
P=CE (14.34)
If the temperature of the polarized pyroelectric
ceramic is raised the molecular dipoles, which are
anyway oscillating about their parallel orienta-
tion, will oscillate through a greater angle. Figure
14.53 shows one molecular dipole of length x and
charge &q. Its electric moment is qx. If. then, the
dipole oscillates through an average angle of iQ
63 the effective length will be z where (14.35)
-7 = scose
The angle 8 will increase with increasing tempera-
ture, thus reducing the electric moment of all the
molecular dipoles. The electric moment or polar-
ization of the whole piece of pyroelectric ceramic
is of course the sum of all the molecular dipoles.
Thus as the temperature rises the polarization of
the whole piece of material gets less.
The Curie point is the temperature at which the
oscillatory energy of the molecular dipoles is such
that they can rotate freely into any position allow-
ing them to return to their random orientation.
As stated above, the electric moment iM of the
whole slice of ceramic is the sum of all the mole-
cular dipole moments:
M = P Ah (14.36)
P where P is the dipole moment per unit volume, 12
is the thickness of the slice and A is the electrode
area; see Figure 14.54.
If the electric charge at the two surfaces of the
slice of pyroelectric ceramic is Qs this has a dipole
moment of Qs . h, so that
Qs = PA (14.37)
If the temperature of the material rises the polar-
ization is reduced and therefore Qs becomes less.
But if the electrodes are connected by an external
circuit to an electrometer or other high impe-
dance detector Qs is normally neutralized by a
(C) charge Q on the electrodes. A reduction of Qs
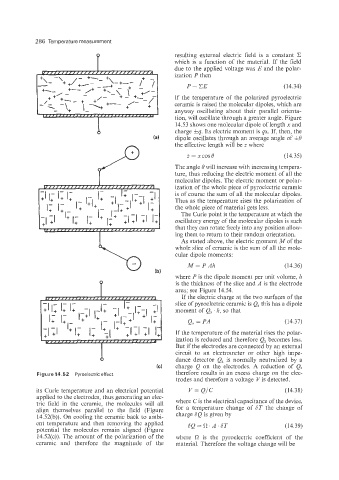
Figure 14.52 Pyroelectric effect. therefore results in an excess charge on the elec-
trodes and therefore a voltage Vis detected.
its Curie temperature and an electrical potential V = QIC (14.38)
applied to the electrodes, thus generating an elec-
tric field in the ceramic, the molecules will all where Cis the electrical capacitance of the device,
align themselves parallel to the field (Figure for a temperature change of ST the change of
14.52(b)). On cooling the ceramic back to ambi- charge SQ is given by
ent temperature and then removing the applied SQ = R. A, ST (14.39)
potential the molecules remain aligned (Figure
14.52(c)). The amount of the polarization of the where 0 is the pyroelectric coefficient of the
ceramic and therefore the magnitude of the material. Therefore the voltage change will be