Page 307 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 307
Measurement techniques: radiation thermometers 291
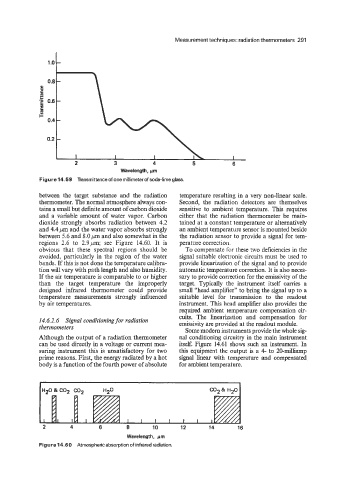
7.0 -
e
I- 0.4 -
0.2 -
I
2 3 4 5 6
Wavelength, pm
Figure 14.59 Transmittanceof one millimeterof soda-limeglass.
between the target substance and the radiation temperature resulting in a very non-linear scale.
thermometer. The normal atmosphere always con- Second, the radiation detectors are themselves
tains a small but definite amount of carbon dioxide sensitive to ambient temperature. This requires
and a variable amount of water vapor. Carbon either that the radiation thermometer be main-
dioxide strongly absorbs radiation between 4.2 tained at a constant temperature or alternatively
and 4.4 ,urn and the water vapor absorbs strongly an ambient temperature sensor is mounted beside
between 5.6 and 8.0pm and also somewhat in the the radiation sensor to provide a signal for tem-
regions 2.6 to 2.9pm; see Figure 14.60. It is perature correction.
obvious that these spectral regions should be To compensate for these two deficiencies in the
avoided, particularly in the region of the water signal suitable electronic circuits must be used to
bands. If this is not done the temperature calibra- provide linearization of the signal and to provide
tion will vary with path length and also humidity. automatic temperature correction. It is also neces-
If the air temperature is comparable to or higher sary to provide correction for the emissivity of the
than the target temperature the improperly target. Typically the instrument itself carries a
designed infrared thermometer could provide small “head amplifier” to bring the signal up to a
temperature measurements strongly influenced suitable level for transmission to the readout
by air temperatures. instrument. This head amplifier also provides the
required ambient temperature compensation cir-
cuits. The linearization and compensation for
14.6.2.6 Signal conditioning for radiation emissivity are provided at the readout module.
thermometers
Some modern instruments provide the whole sig-
AIthough the output of a radiation thermometer nal conditioning circuitry in the main instrument
can be used directly in a voltage or current mea- itself. Figure 14.61 shows such an instrument. In
suring instrument this is unsatisfactory for two this equipment the output is a 4- to 20-milliamp
pike reasons. First, the energy radiated by a hot signal linear with temperzture and compensated
body is a function of the fourth power of absolute for ambient temperature.
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Wavelength, pm
Figure 14.60 Atmosphericabsorption of infrared radiation.