Page 326 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 326
310 Chemical analysis: introduction 15.3.1.5 Differential pulse polrrrogrnphy
ii The most important of modern polarographic
techniques is that of differential pulse polaro-
graphy. Here a 25 or 50mV amplitude pulse
I is superimposed at fixed time intervals on the
normal linear increasing voltage of 2 or
I 5mVs-', with the mercury drop being dis-
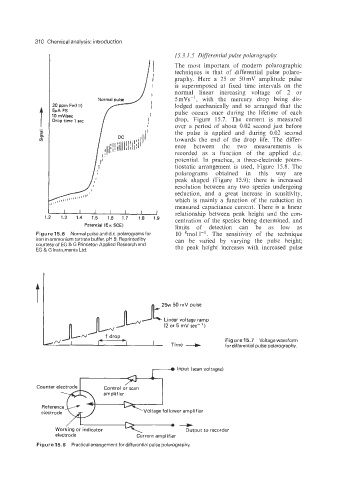
20 ppm Fe(l I I) I lodged mechanically and so arranged that the
5#A FS pulse occurs once during the lifetime of each
10 rnV/sec I
Drop time 1 sec I drop, Figure 15.7. The current is measured
over a period of about 0.02 second just before
the pulse is applied and during 0.02 second
towards the end of the drop life. The differ-
ence between the two measurements is
recorded as a function of the applied d.c.
potential. In practice, a three-electrode poten-
tiostatic arrangement is used, Figure 15.8. The
polarograms obtained in this way are
peak shaped (Figure 15.9); there is increased
resolution between any two species undergoing
reduction, and a great increase in sensitivity,
which is mainly a function of the reduction in
measured capacitance current. There is a linear
I I I I I I I 1 relationship between peak height and the con-
1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 centration of the species being determined, and
Potential (E v. SCE) limits of detection can be as low as
Figure15.6 Normal pulse and d.c. polarogramsfor 10~8mol 1-'. The sensitivity of the technique
iron in ammonium tartrate buffer, pH 9. Reprinted by can be varied by varying the pulse height;
courtesy of EG & G Princeton Applied Research and the peak height increases with increased pulse
EG & G Instruments Ltd.
+I
25w 50 mV pulse
Linear voltage ramp
(2 or 5 mV sec- ' )
I Time + Figure 15.7 Voltagewaveform
for differential pulse polarography.
Input (scan voltages)
Counter electrode Control or scan
amplifier
Voltage follower amplifier
r\ *+
Working or indicator v\ Output to recorder
electrode Current amplifier
Figure 15.8 Practical arrangement for differential pulse polarography.