Page 408 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 408
Detectors 391
gas streams or as a gas-chromatographic detector. atoms, or between metastable atoms, which may
When used as a detector in gas chromatography also result in ion formation.
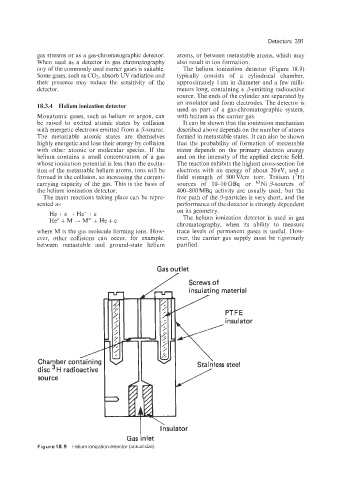
any of the commonly used carrier gases is suitable. The helium ionization detector (Figure 18.9)
Some gases, such as COz, absorb W radiation and typically consists of a cylindrical chamber,
their presence may reduce the sensitivity of the approximately 1 cm in diameter and a few milli-
detector. meters long, containing a p-emitting radioactive
source. The ends of the cylinder are separated by
an insulator and form electrodes. The detector is
18.3.4 Helium ionization detector used as part of a gas-chromatographic system,
Monatomic gases, such as helium or argon, can with helium as the carrier gas.
be raised to excited atomic states by collision It can be shown that the ionization mechanism
with energetic electrons emitted from a ,O-source. described above depends on the number of atoms
The metastable atomic states are themselves formed in metastable states. It can also be shown
highly energetic and lose their energy by collision that the probability of formation of metastable
with othe:: atomic or molecular species. If the states depends on the primary electron energy
helium contains a small concentration of a gas and on the intensity of the applied electric field.
whose ionization potential is less than the excita- The reaction exhibits the highest cross-section for
tion of the metastable helium atoms, ions will be electrons with an energy of about 20eV, and a
formed in the collision, so increasing the current- field strength of 5OOV/m torr. Tritium (3H)
carrying capacity of the gas. This is the basis of sources of 10-10GBq or 63Ni p-sources of
the helium ionization detector. 400-800 MBq activity are usually used, but the
The main reactions taking place can be repre- free path of the $particles is very short, and the
sented as performance of the detector is strongly dependent
on its geometry.
He + e + He* +e The helium ionization detector is used in gas
He* + M + M+ +He + e
chromatography, when its ability to measure
where M is the gas molecule forming ions. How- trace levels of permanent gases is useful. How-
ever, other collisions can occur, for example, ever, the carrier gas supply must be rigorously
between metastable and ground-state helium purified.
Gas outlet
Screws of
insulating material
/ PTFE
/
Chamber containing
disc H radioactive
source
I Insulator
Gas inlet
Figure 18.9 Helium ionization detector (actual size)