Page 181 -
P. 181
Process 163
When the billing step is completed, accounts receivable reconciliation
and sales revenue accounts in the general ledger are updated. The accounts
receivable account is debited by the amount of the invoice, which is the
amount the customer owes, and the sales revenue account is credited by
the same amount. Recall, however, that because accounts receivable is a rec-
onciliation account, the amount of the invoice cannot be posted directly to
the accounts receivable account. Instead, the amount is posted through the
cor responding subledger account, in this case, the customer account. An open
item is created in the customer’s account via a debit entry, which automatically
creates an entry in the accounts receivable account. In addition to postings to
the general ledger, an FI document is created to record these data. Finally,
because the billing step increases the amount receivable from the customer,
the available credit decreases by a corresponding amount.
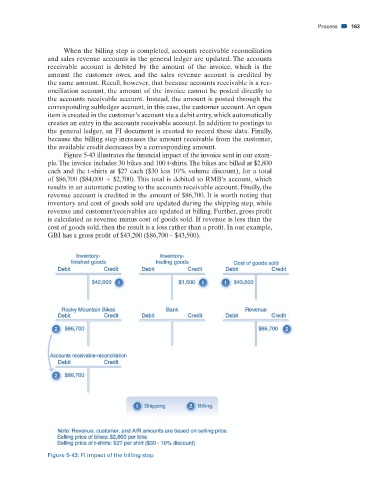
Figure 5-43 illustrates the fi nancial impact of the invoice sent in our exam-
ple. The invoice includes 30 bikes and 100 t-shirts. The bikes are billed at $2,800
each and the t-shirts at $27 each ($30 less 10% volume discount), for a total
of $86,700 ($84,000 $2,700). This total is debited to RMB’s account, which
results in an automatic posting to the accounts receivable account. Finally, the
revenue account is credited in the amount of $86,700. It is worth noting that
inventory and cost of goods sold are updated during the shipping step, while
revenue and customer/receivables are updated at billing. Further, gross profi t
is calculated as revenue minus cost of goods sold. If revenue is less than the
cost of goods sold, then the result is a loss rather than a profi t. In our example,
GBI has a gross profi t of $43,200 ($86,700 – $43,500).
Figure 5-43: FI impact of the billing step
31/01/11 6:39 AM
CH005.indd 163 31/01/11 6:39 AM
CH005.indd 163