Page 132 - Integrated Wireless Propagation Models
P. 132
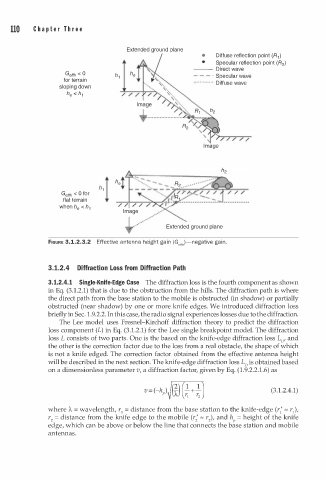
110 C h a p t e r T h r e e
Extended ground plane
• Diffuse reflection point (R1 )
• Specular reflection point (R2 )
--- Direct wave
Geffh < 0 - · Specular wave
for terrain - - Diffuse wave
•• · ••·• • ·•· ·•
sloping down
h
h e < 1
/
I m age
Getth < 0 for
flat terrain
when h e < h 1
Extended ground plane
FIGURE 3.1.2.3.2 Effective a n tenna height gain (Geffh)-negative gai n .
3.1.2.4 Diffraction Loss from Diffraction Path
3. 1.2.4. 1 Single-Knife-Edge Case The diffraction loss is the fourth component as shown
in Eq. (3.1.2.1) that is due to the obstruction from the hills. The diffraction path is where
the direct path from the base station to the mobile is obstructed (in shadow) or partially
obstructed (near shadow) by one or more knife edges. We introduced diffraction loss
1
briefly in Sec. . 9.2.2. In this case, the radio signal experiences losses due to the diffraction.
The Lee model uses Fresnel-Kirchoff diffraction theory to predict the diffraction
loss component (L) in Eq. (3 1 . 2.1) for the Lee single breakpoint model. The diffraction
.
loss L consists of two parts. One is the based on the knife-edge diffraction loss L0, and
the other is the correction factor due to the loss from a real obstacle, the shape of which
is not a knife edged. The correction factor obtained from the effective antenna height
will be described in the next section. The knife-edge diffraction loss L0 is obtained based
on a dimensionless parameter v, a diffraction factor, given by Eq. (1.9.2.2.1.6) as
(3 1 .2.4.1)
.
'A
where = wavelength, r = distance from the base station to the knife-edge (r; "' r ),
1
1
r2 = distance from the knife edge to the mobile (r; "' r2), and hP h eight of the knife
=
edge, which can be above or below the line that connects the base station and mobile
antennas.