Page 330 - Integrated Wireless Propagation Models
P. 330
308 C h a p t e r F i v e
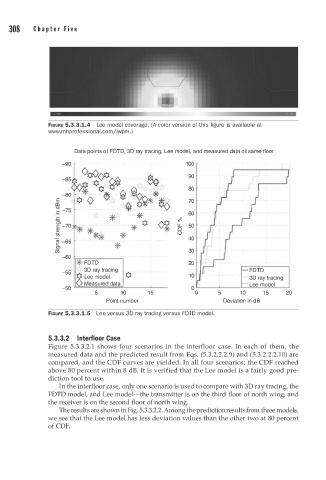
FIGURE 5.3.3.1.4 Lee model coverage. (A color version of this figure is available at
www.mhprofessional.comjiwpm. )
Data points f FDTD, 3D ray tracing, Lee model, and measured data f same floor
o
o
-90 1 0 0
o oO oo 90
¢ 0 ifJ �
* 0 � 80
o o � � � � * � 70
60
* * �
0
* 0 LL. 50
� 0
0
* ** * 40
� -65
0> *
Ui 30
-60
* FDTD 20
-55 3D ray tracing - FDTD
Lee model 0 1 0 3D ray tracing
Measured data - Lee model
-50 0
5 1 0 1 5 0 5 1 0 1 5 20
Point number Deviation in B
d
FIGURE 5.3.3.1.5 Lee versus 3D ray tracing versus FDTD model .
5.3.3.2 lnterfloor Case
Figure 5.3.3.2.1 shows four scenarios in the interfloor case. In each of them, the
measured data and the predicted result from Eqs. (5.3.2.2.2.9) and (5.3.2.2.2.10) are
compared, and the CDF curves are yielded. In all four scenarios; the CDF reached
above 80 percent within 8 dB. It is verified that the Lee model is a fairly good pre
diction tool to use.
In the interfloor case, only one scenario is used to compare with 3D ray tracing, the
FDTD model, and Lee model-the transmitter is on the third floor of north wing, and
the receiver is on the second floor of north wing.
The results are shown in Fig. 5.3.3.2.2. Among the prediction results from three models,
we see that the Lee model has less deviation values than the other two at 80 percent
of CDF.