Page 76 - Intro to Tensor Calculus
P. 76
71
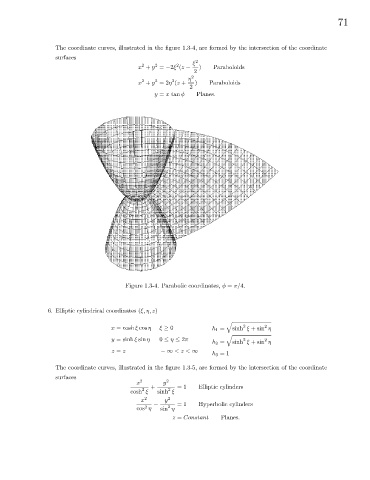
The coordinate curves, illustrated in the figure 1.3-4, are formed by the intersection of the coordinate
surfaces
ξ 2
2 2 2
x + y = −2ξ (z − ) Paraboloids
2
η 2
2 2 2
x + y =2η (z + ) Paraboloids
2
y = x tan φ Planes.
Figure 1.3-4. Parabolic coordinates, φ = π/4.
6. Elliptic cylindrical coordinates (ξ, η, z)
q
2
2
x =cosh ξ cos η ξ ≥ 0 h 1 = sinh ξ +sin η
q
y = sinh ξ sin η 0 ≤ η ≤ 2π 2 2
h 2 = sinh ξ +sin η
z = z −∞ <z < ∞
h 3 =1
The coordinate curves, illustrated in the figure 1.3-5, are formed by the intersection of the coordinate
surfaces
x 2 + y 2 = 1 Elliptic cylinders
2
2
cosh ξ sinh ξ
x 2 y 2
− 2 = 1 Hyperbolic cylinders
2
cos η sin η
z = Constant Planes.