Page 324 - Introduction to Marine Engineering
P. 324
298 Instrumentation and control
A sample is drawn off from the overboard discharge and passes
through a sample cell (Figure 15.23). An ultra-violet light is directed at
the sample and the fluorescence is monitored by a photoelectric cell.
The measured value is compared with the maximum desired value in
the controller/recorder. Where an excessive level of contamination is
detected an alarm is sounded and diverting valves are operated. The
discharging liquid is then passed to a slop tank.
Control theory
To control a device or system is to be able to adjust or vary the
parameters which affect it. This can be achieved manually or
automatically, depending upon the arrangements made in the system.
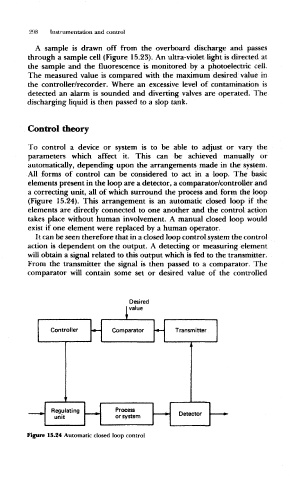
All forms of control can be considered to act in a loop. The basic
elements present in the loop are a detector, a comparator/controller and
a correcting unit, all of which surround the process and form the loop
(Figure 15.24). This arrangement is an automatic closed loop if the
elements are directly connected to one another and the control action
takes place without human involvement. A manual closed loop would
exist if one element were replaced by a human operator.
It can be seen therefore that in a closed loop control system the control
action is dependent on the output. A detecting or measuring element
will obtain a signal related to this output which is fed to the transmitter.
From the transmitter the signal is then passed to a comparator. The
comparator will contain some set or desired value of the controlled
Desired
value
Figure 15.24 Automatic closed loop control