Page 381 - Introduction to Marine Engineering
P. 381
Appendix 351
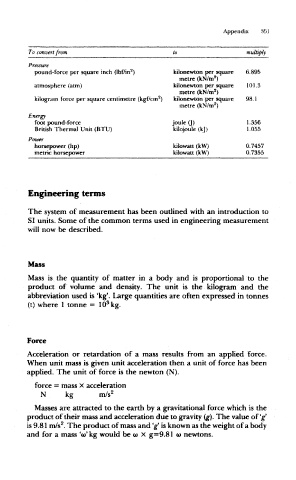
To convert from multiply
Pressure
2
pound-force per square inch (lbf/in ) kilonewton per square 6.895
2
metre (kN/m )
atmosphere (attn) kilonewton per square 101.3
2
metre (kN/m )
2
kilogram force per square centimetre (kgf/cm ) kilonewton per square 98.1
2
metre (kN/m )
Energy
foot pound-force joule (J) 1.356
British Thermal Unit (BTU) kilojoule (kj) 1.055
Power
horsepower (hp) kilowatt (kW) 0.7457
metric horsepower kilowatt (kW) 0.7355
Engineering terms
The system of measurement has been outlined with an introduction to
SI units. Some of the common terms used in engineering measurement
will now be described.
Mass
Mass is the quantity of matter in a body and is proportional to the
product of volume and density. The unit is the kilogram and the
abbreviation used is 'kg'. Large quantities are often expressed in tonnes
s
(t) where 1 tonne = 10 kg.
Force
Acceleration or retardation of a mass results from an applied force.
When unit mass is given unit acceleration then a unit of force has been
applied. The unit of force is the newton (N).
force = mass X acceleration
2
N kg m/s
Masses are attracted to the earth by a gravitational force which is the
product of their mass and acceleration due to gravity (g). The value of'g'
2
is 9.81 m/s . The product of mass and 'g' is known as the weight of a body
and for a mass 'w'kg would be w x g=9.81 <u newtons.