Page 85 - Introduction to Microcontrollers Architecture, Programming, and Interfacing of The Motorola 68HC12
P. 85
62 Chapter 3 Addressing Modes
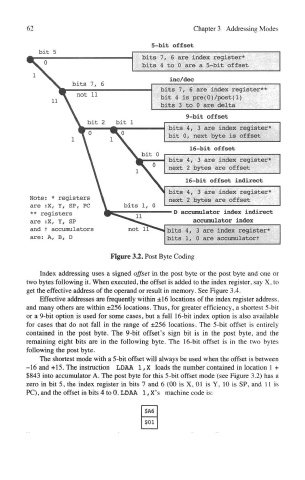
Figure 3.2. Post Byte Coding
Index addressing uses a signed offset in the post byte or the post byte and one or
two bytes following it. When executed, the offset is added to the index register, say X, to
get the effective address of the operand or result in memory. See Figure 3.4.
Effective addresses are frequently within ±16 locations of the index register address,
and many others are within ±256 locations. Thus, for greater efficiency, a shortest 5-bit
or a 9-bit option is used for some cases, but a full 16-bit index option is also available
for cases that do not fall in the range of ±256 locations. The 5-bit offset is entirely
contained in the post byte. The 9-bit offset's sign bit is in the post byte, and the
remaining eight bits are in the following byte. The 16-bit offset is in the two bytes
following the post byte.
The shortest mode with a 5-bit offset will always be used when the offset is between
-16 and +15. The instruction LDAA 1, X loads the number contained in location 1 +
$843 into accumulator A. The post byte for this 5-bit offset mode (see Figure 3.2) has a
zero in bit 5, the index register in bits 7 and 6 (00 is X, 01 is Y, 10 is SP, and 11 is
PC),and the offset in bits 4 toO. LDAA l,X's machine code is: