Page 180 - System on Package_ Miniaturization of the Entire System
P. 180
Mixed-Signal (SOP) Design 155
4.1.2 Importance of Integration in Mobile Applications
In this chapter, mixed-signal design issues in the context of handsets and other mobile
applications will be discussed. The market drivers for handsets are (1) size, (2)
performance, (3) cost, and (4) reliability, not necessarily in that order. With the trend
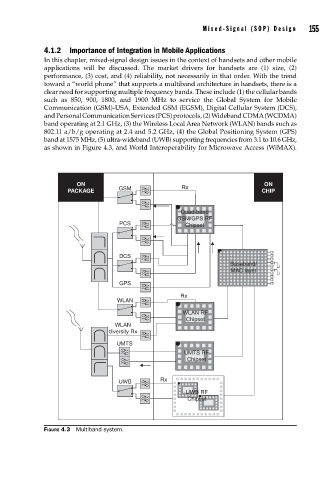
toward a “world phone” that supports a multiband architecture in handsets, there is a
clear need for supporting multiple frequency bands. These include (1) the cellular bands
such as 850, 900, 1800, and 1900 MHz to service the Global System for Mobile
Communication (GSM)-USA, Extended GSM (EGSM), Digital Cellular System (DCS),
and Personal Communication Services (PCS) protocols, (2) Wideband CDMA (WCDMA)
band operating at 2.1 GHz, (3) the Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) bands such as
802.11 a/b/g operating at 2.4 and 5.2 GHz, (4) the Global Positioning System (GPS)
band at 1575 MHz, (5) ultra-wideband (UWB) supporting frequencies from 3.1 to 10.6 GHz,
as shown in Figure 4.3, and World Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX).
ON Rx ON
PACKAGE GSM CHIP
Quad-band
GSM/GPS RF
PCS Chipset
DCS
Baseband/
MAC layer
GPS
Rx
WLAN
WLAN RF
Chipset
WLAN
diversity Rx
UMTS
UMTS RF
Chipset
Rx
UWB
UWB RF
Chipset
FIGURE 4.3 Multiband system.