Page 234 - System on Package_ Miniaturization of the Entire System
P. 234
208 Cha pte r F o u r
12 10 Extrapolated
Extrapolated
Interpolated response response Interpolated response response
10
5
Real (Y22) 8 6 Imaginary (Y22) −5 0
4 Solid line: Orginal data Solid line: Orginal data
Dotted line: Macromodel Dotted line: Macromodel
−10
2
−15
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Frequency (GHz) Frequency (GHz)
3
1.0 Extrapolated Extrapolated
Interpolated response response Interpolated response response
2
0.5 1
Real (Y23) 0 Imaginary (Y22) 0
−0.5 −1
Solid line: Orginal data Solid line: Orginal data
Dotted line: Macromodel Dotted line: Macromodel
−1.0 −2
−3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Frequency (GHz) Frequency (GHz)
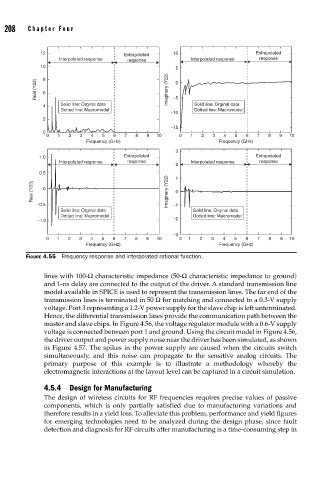
FIGURE 4.55 Frequency response and interpolated rational function.
lines with 100-Ω characteristic impedance (50-Ω characteristic impedance to ground)
and 1-ns delay are connected to the output of the driver. A standard transmission line
model available in SPICE is used to represent the transmission lines. The far end of the
transmission lines is terminated in 50 Ω for matching and connected to a 0.3-V supply
voltage. Port 3 representing a 1.2-V power supply for the slave chip is left unterminated.
Hence, the differential transmission lines provide the communication path between the
master and slave chips. In Figure 4.56, the voltage regulator module with a 0.6-V supply
voltage is connected between port 1 and ground. Using the circuit model in Figure 4.56,
the driver output and power supply noise near the driver has been simulated, as shown
in Figure 4.57. The spikes in the power supply are caused when the circuits switch
simultaneously, and this noise can propagate to the sensitive analog circuits. The
primary purpose of this example is to illustrate a methodology whereby the
electromagnetic interactions at the layout level can be captured in a circuit simulation.
4.5.4 Design for Manufacturing
The design of wireless circuits for RF frequencies requires precise values of passive
components, which is only partially satisfied due to manufacturing variations and
therefore results in a yield loss. To alleviate this problem, performance and yield figures
for emerging technologies need to be analyzed during the design phase, since fault
detection and diagnosis for RF circuits after manufacturing is a time-consuming step in