Page 233 - System on Package_ Miniaturization of the Entire System
P. 233
Mixed-Signal (SOP) Design 207
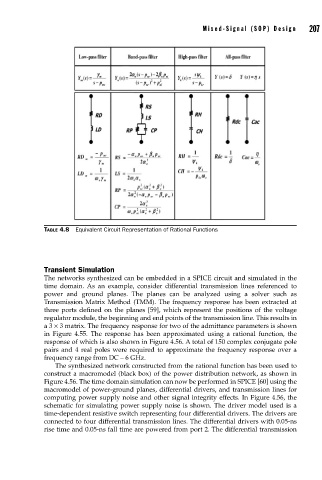
TABLE 4.8 Equivalent Circuit Representation of Rational Functions
Transient Simulation
The networks synthesized can be embedded in a SPICE circuit and simulated in the
time domain. As an example, consider differential transmission lines referenced to
power and ground planes. The planes can be analyzed using a solver such as
Transmission Matrix Method (TMM). The frequency response has been extracted at
three ports defined on the planes [59], which represent the positions of the voltage
regulator module, the beginning and end points of the transmission line. This results in
a 3 × 3 matrix. The frequency response for two of the admittance parameters is shown
in Figure 4.55. The response has been approximated using a rational function, the
response of which is also shown in Figure 4.56. A total of 150 complex conjugate pole
pairs and 4 real poles were required to approximate the frequency response over a
frequency range from DC – 6 GHz.
The synthesized network constructed from the rational function has been used to
construct a macromodel (black box) of the power distribution network, as shown in
Figure 4.56. The time domain simulation can now be performed in SPICE [60] using the
macromodel of power-ground planes, differential drivers, and transmission lines for
computing power supply noise and other signal integrity effects. In Figure 4.56, the
schematic for simulating power supply noise is shown. The driver model used is a
time-dependent resistive switch representing four differential drivers. The drivers are
connected to four differential transmission lines. The differential drivers with 0.05-ns
rise time and 0.05-ns fall time are powered from port 2. The differential transmission