Page 368 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 368
Cleanrooms 347
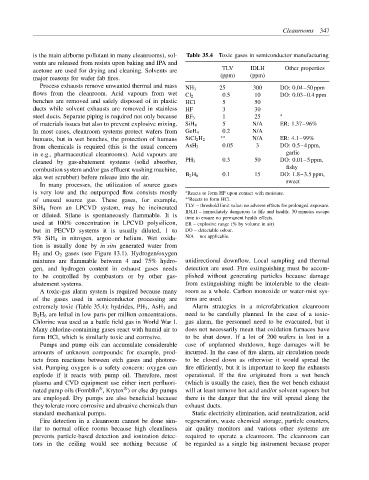
is the main airborne pollutant in many cleanrooms), sol- Table 35.4 Toxic gases in semiconductor manufacturing
vents are released from resists upon baking and IPA and
TLV IDLH Other properties
acetone are used for drying and cleaning. Solvents are
(ppm) (ppm)
major reasons for wafer fab fires.
Process exhausts remove unwanted thermal and mass
NH 3 25 300 DO: 0.04–50 ppm
flows from the cleanroom. Acid vapours from wet 0.5 10 DO: 0.03–0.4 ppm
Cl 2
benches are removed and safely disposed of in plastic HCl 5 50
ducts while solvent exhausts are removed in stainless HF 3 30
steel ducts. Separate piping is required not only because BF 3 1 25 ∗
of materials issues but also to prevent explosive mixing. SiH 4 5 N/A ER: 1.37–96%
In most cases, cleanroom systems protect wafers from GeH 4 0.2 N/A
humans, but in wet benches, the protection of humans SiCl 2 H 2 ∗∗ N/A ER: 4.1–99%
from chemicals is required (this is the usual concern AsH 3 0.05 3 DO: 0.5–4 ppm,
in e.g., pharmaceutical cleanrooms). Acid vapours are garlic
cleaned by gas-abatement systems (solid absorber, PH 3 0.3 50 DO: 0.01–5 ppm,
combustion system and/or gas effluent washing machine, fishy
aka wet scrubber) before release into the air. B 2 H 6 0.1 15 DO: 1.8–3.5 ppm,
In many processes, the utilization of source gases sweet
is very low and the outpumped flow consists mostly ∗ Reacts to form HF upon contact with moisture.
of unused source gas. These gases, for example, ∗∗ Reacts to form HCl.
SiH 4 from an LPCVD system, may be incinerated TLV – threshold limit value: no adverse effects for prolonged exposure.
IDLH – immediately dangerous to life and health: 30 minutes escape
or diluted. Silane is spontaneously flammable. It is
time to ensure no permanent health effects.
used at 100% concentration in LPCVD polysilicon, ER – explosive range (% by volume in air).
but in PECVD systems it is usually diluted, 1 to DO – detectable odour.
5% SiH 4 in nitrogen, argon or helium. Wet oxida- N/A – not applicable.
tion is usually done by in situ generated water from
H 2 and O 2 gases (see Figure 13.1). Hydrogen/oxygen
mixtures are flammable between 4 and 75% hydro- unidirectional downflow. Local sampling and thermal
gen, and hydrogen content in exhaust gases needs detection are used. Fire extinguishing must be accom-
to be controlled by combustors or by other gas- plished without generating particles because damage
abatement systems. from extinguishing might be intolerable to the clean-
A toxic-gas alarm system is required because many room as a whole. Carbon monoxide or water-mist sys-
of the gases used in semiconductor processing are tems are used.
extremely toxic (Table 35.4): hydrides, PH 3 , AsH 3 and Alarm strategies in a microfabrication cleanroom
B 2 H 6 are lethal in low parts per million concentrations. need to be carefully planned. In the case of a toxic-
Chlorine was used as a battle field gas in World War I. gas alarm, the personnel need to be evacuated, but it
Many chlorine-containing gases react with humid air to does not necessarily mean that oxidation furnaces have
form HCl, which is similarly toxic and corrosive. to be shut down. If a lot of 200 wafers is lost in a
Pumps and pump oils can accumulate considerable case of unplanned shutdown, huge damages will be
amounts of unknown compounds: for example, prod- incurred. In the case of fire alarm, air circulation needs
ucts from reactions between etch gases and photore- to be closed down as otherwise it would spread the
sist. Pumping oxygen is a safety concern: oxygen can fire efficiently, but it is important to keep the exhausts
explode if it reacts with pump oil. Therefore, most operational. If the fire originated from a wet bench
plasma and CVD equipment use either inert perfluori- (which is usually the case), then the wet bench exhaust
nated pump oils (Fomblin , Krytox ) or else dry pumps will at least remove hot acid and/or solvent vapours but
are employed. Dry pumps are also beneficial because there is the danger that the fire will spread along the
they tolerate more corrosive and abrasive chemicals than exhaust ducts.
standard mechanical pumps. Static electricity elimination, acid neutralization, acid
Fire detection in a cleanroom cannot be done sim- regeneration, waste chemical storage, particle counters,
ilar to normal office rooms because high cleanliness air quality monitors and various other systems are
prevents particle-based detection and ionization detec- required to operate a cleanroom. The cleanroom can
tors in the ceiling would see nothing because of be regarded as a single big instrument because proper