Page 398 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 398
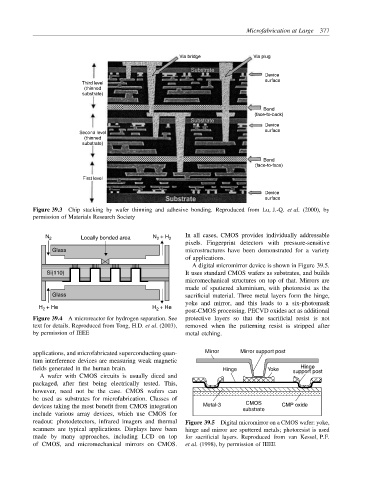
Microfabrication at Large 377
Via bridge Via plug
Device
surface
Third level
(thinned
substrate)
Bond
(face-to-back)
Device
Second level surface
(thinned
substrate)
Bond
(face-to-face)
First level
Device
surface
Figure 39.3 Chip stacking by wafer thinning and adhesive bonding. Reproduced from Lu, J.-Q. et al. (2000), by
permission of Materials Research Society
N 2 Locally bonded area N + H 2 In all cases, CMOS provides individually addressable
2
pixels. Fingerprint detectors with pressure-sensitive
Glass microstructures have been demonstrated for a variety
of applications.
A digital micromirror device is shown in Figure 39.5.
Si(110) It uses standard CMOS wafers as substrates, and builds
micromechanical structures on top of that. Mirrors are
made of sputtered aluminium, with photoresist as the
Glass sacrificial material. Three metal layers form the hinge,
yoke and mirror, and this leads to a six-photomask
H + He H + He
2
2
post-CMOS processing. PECVD oxides act as additional
Figure 39.4 A microreactor for hydrogen separation. See protective layers so that the sacrificial resist is not
text for details. Reproduced from Tong, H.D. et al. (2003), removed when the patterning resist is stripped after
by permission of IEEE metal etching.
applications, and microfabricated superconducting quan- Mirror Mirror support post
tum interference devices are measuring weak magnetic
Hinge
fields generated in the human brain. Hinge Yoke support post
A wafer with CMOS circuits is usually diced and
packaged, after first being electrically tested. This,
however, need not be the case. CMOS wafers can
be used as substrates for microfabrication. Classes of
CMOS
devices taking the most benefit from CMOS integration Metal-3 substrate CMP oxide
include various array devices, which use CMOS for
readout: photodetectors, infrared imagers and thermal Figure 39.5 Digital micromirror on a CMOS wafer: yoke,
scanners are typical applications. Displays have been hinge and mirror are sputtered metals; photoresist is used
made by many approaches, including LCD on top for sacrificial layers. Reproduced from van Kessel, P.F.
of CMOS, and micromechanical mirrors on CMOS. et al. (1998), by permission of IEEE