Page 34 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 34
BASIC CONCEPTS 1.11
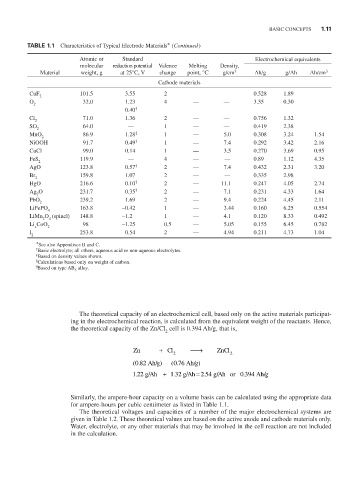
TABLE 1.1 Characteristics of Typical Electrode Materials* (Continued )
Atomic or Standard Electrochemical equivalents
molecular reduction potential Valence Melting Density,
Material weight, g at 25°C, V change point, °C g/cm 3 Ah/g g/Ah Ah/cm 3
Cathode materials
CuF 2 101.5 3.55 2 0.528 1.89
O 32.0 1.23 4 — — 3.35 0.30
2
0.40 †
Cl 71.0 1.36 2 — — 0.756 1.32
2
SO 64.0 — 1 — — 0.419 2.38
2
MnO 86.9 1.28 ‡ 1 — 5.0 0.308 3.24 1.54
2
NiOOH 91.7 0.49 † 1 — 7.4 0.292 3.42 2.16
CuCl 99.0 0.14 1 — 3.5 0.270 3.69 0.95
FeS 2 119.9 — 4 — — 0.89 1.12 4.35
AgO 123.8 0.57 † 2 — 7.4 0.432 2.31 3.20
Br 159.8 1.07 2 — — 0.335 2.98
2
HgO 216.6 0.10 † 2 — 11.1 0.247 4.05 2.74
Ag O 231.7 0.35 † 2 — 7.1 0.231 4.33 1.64
2
PbO 239.2 1.69 2 — 9.4 0.224 4.45 2.11
2
LiFePO 163.8 ∼0.42 1 — 3.44 0.160 6.25 0.554
4
LiMn O (spinel) 148.8 ∼1.2 1 — 4.1 0.120 8.33 0.492
2 4
Li CoO 2 98 ∼1.25 0.5 — 5.05 0.155 6.45 0.782
x
I 253.8 0.54 2 — 4.94 0.211 4.73 1.04
2
*See also Appendixes B and C.
† Basic electrolyte; all others, aqueous acid or non-aqueous electrolytes.
‡ Based on density values shown.
§ Calculations based only on weight of carbon.
¶ Based on type AB alloy.
5
The theoretical capacity of an electrochemical cell, based only on the active materials participat-
ing in the electrochemical reaction, is calculated from the equivalent weight of the reactants. Hence,
the theoretical capacity of the Zn/Cl cell is 0.394 Ah/g, that is,
2
Zn + Cl 2 → ZnCl 2
.
082
(. Ah/g) ( 0 76 Ah/g)
.
.
.
122 g/Ah + 1.332 g/Ah = 254 g/Ah or 0 394 Ah/g
Similarly, the ampere-hour capacity on a volume basis can be calculated using the appropriate data
for ampere-hours per cubic centimeter as listed in Table 1.1.
The theoretical voltages and capacities of a number of the major electrochemical systems are
given in Table 1.2. These theoretical values are based on the active anode and cathode materials only.
Water, electrolyte, or any other materials that may be involved in the cell reaction are not included
in the calculation.