Page 160 - Low Temperature Energy Systems with Applications of Renewable Energy
P. 160
150 Low-Temperature Energy Systems with Applications of Renewable Energy
at low drying temperatures of thermosensitive food products makes it possible to use
heat pump technology in combination with pneumatic, conveyor, or vibration drying
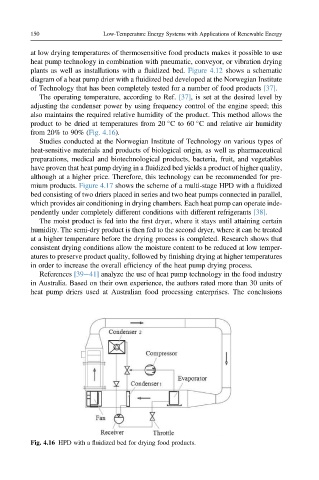
plants as well as installations with a fluidized bed. Figure 4.12 shows a schematic
diagram of a heat pump drier with a fluidized bed developed at the Norwegian Institute
of Technology that has been completely tested for a number of food products [37].
The operating temperature, according to Ref. [37], is set at the desired level by
adjusting the condenser power by using frequency control of the engine speed; this
also maintains the required relative humidity of the product. This method allows the
product to be dried at temperatures from 20 Cto60 C and relative air humidity
from 20% to 90% (Fig. 4.16).
Studies conducted at the Norwegian Institute of Technology on various types of
heat-sensitive materials and products of biological origin, as well as pharmaceutical
preparations, medical and biotechnological products, bacteria, fruit, and vegetables
have proven that heat pump drying in a fluidized bed yields a product of higher quality,
although at a higher price. Therefore, this technology can be recommended for pre-
mium products. Figure 4.17 shows the scheme of a multi-stage HPD with a fluidized
bed consisting of two driers placed in series and two heat pumps connected in parallel,
which provides air conditioning in drying chambers. Each heat pump can operate inde-
pendently under completely different conditions with different refrigerants [38].
The moist product is fed into the first dryer, where it stays until attaining certain
humidity. The semi-dry product is then fed to the second dryer, where it can be treated
at a higher temperature before the drying process is completed. Research shows that
consistent drying conditions allow the moisture content to be reduced at low temper-
atures to preserve product quality, followed by finishing drying at higher temperatures
in order to increase the overall efficiency of the heat pump drying process.
References [39e41] analyze the use of heat pump technology in the food industry
in Australia. Based on their own experience, the authors rated more than 30 units of
heat pump driers used at Australian food processing enterprises. The conclusions
Fig. 4.16 HPD with a fluidized bed for drying food products.