Page 53 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 53
38 ——— MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
1.18 INPUT/OUTPUT IN MATLAB
In this section, we present some of the many available commands in MATLAB for reading data from an
external file into a MATLAB matrix, or writing the numbers computed in MATLAB into such an external file.
1.18.1 The fopen Statement
To have the MATLAB read or write a separate data file of numerical values, we need to connect the file to the
executing MATLAB program. The MATLAB functions used are summarized in Table 1.32.
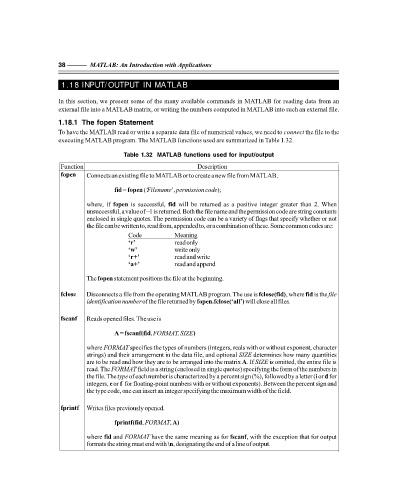
Table 1.32 MATLAB functions used for input/output
Function Description
fopen Connects an existing file to MATLAB or to create a new file from MATLAB.
(‘
fid = fopen Filename permission code );
’,
where, if fopen is successful, fid will be returned as a positive integer greater than 2. When
unsuccessful, a value of –1 is returned. Both the file name and the permission code are string constants
enclosed in single quotes. The permission code can be a variety of flags that specify whether or not
the file can be written to, read from, appended to, or a combination of these. Some common codes are:
Code Meaning
‘r’ read only
‘’ write only
w
‘ r+’ read and write
‘ a+’ read and append
The fopen statement positions the file at the beginning.
fclose Disconnects a file from the operating MATLAB program. The use is fclose(fid) , where fid is the file
identification number of the file returned by fopen.fclose(‘all’) will close all files.
fscanf Reads opened files. The use is
A = fscanf(fid FORMAT, SIZE )
,
where FORMAT specifies the types of numbers (integers, reals with or without exponent, character
strings) and their arrangement in the data file, and optional SIZE determines how many quantities
are to be read and how they are to be arranged into the matrix . If SIZE is omitted, the entire file is
A
read. The FORMAT field is a string (enclosed in single quotes) specifying the form of the numbers in
d
i
the file. The type of each number is characterized by a percent sign (%), followed by a letter ( or for
f
e
integers, or for floating-point numbers with or without exponents). Between the percent sign and
the type code, one can insert an integer specifying the maximum width of the field.
fprintf Writes files previously opened.
fprintf(fid , FORMAT , A)
where fid and FORMAT have the same meaning as for fscanf , with the exception that for output
formats the string must end with , designating the end of a line of output.
\n
F:\Final Book\Sanjay\IIIrd Printout\Dt. 10-03-09