Page 55 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 55
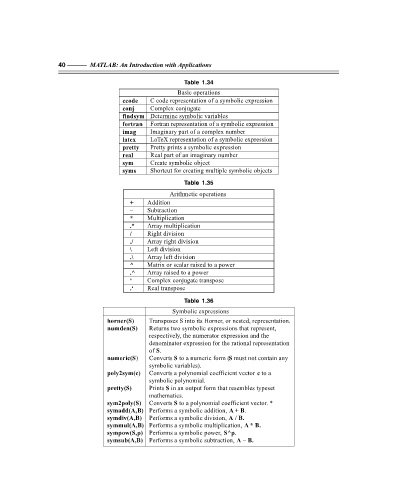
40 ——— MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Table 1.34
Basic operations
ccode C code representation of a symbolic expression
conj Complex conjugate
findsym Determine symbolic variables
fortran Fortran representation of a symbolic expression
imag Imaginary part of a complex number
latex LaTeX representation of a symbolic expression
pretty Pretty prints a symbolic expression
real Real part of an imaginary number
sym Create symbolic object
syms Shortcut for creating multiple symbolic objects
Table 1.35
Arithmetic operations
+ Addition
– Subtraction
* Multiplication
.* Array multiplication
/ Right division
./ Array right division
\ Left division
.\ Array left division
^ Matrix or scalar raised to a power
.^ Array raised to a power
‘ Complex conjugate transpose
.‘ Real transpose
Table 1.36
Symbolic expressions
horner(S) Transposes S into its Horner, or nested, representation.
numden(S) Returns two symbolic expressions that represent,
respectively, the numerator expression and the
denominator expression for the rational representation
of S.
S
numeric(S) Converts to a numeric form (S must not contain any
symbolic variables).
poly2sym(c) Converts a polynomial coefficient vector c to a
symbolic polynomial.
pretty(S) Prints S in an output form that resembles typeset
mathematics.
sym2poly(S) Converts S to a polynomial coefficient vector. *
symadd(A,B) Performs a symbolic addition, A + B.
symdiv(A,B) Performs a symbolic division, A / B.
symmul(A,B) Performs a symbolic multiplication, A * B.
sympow(S,p) Performs a symbolic power, S^p.
symsub(A,B) Performs a symbolic subtraction, A – B.
F:\Final Book\Sanjay\IIIrd Printout\Dt. 10-03-09