Page 177 - MATLAB Recipes for Earth Sciences
P. 177
172 7 Spatial Data
v = -40 : 10 : 40;
contourf(XI,YI,ZI,v)
caxis([-40 40]), colorbar, hold on
plot(data(:,1),data(:,2),'ko')
text(data(:,1)+1,data(:,2),labels)
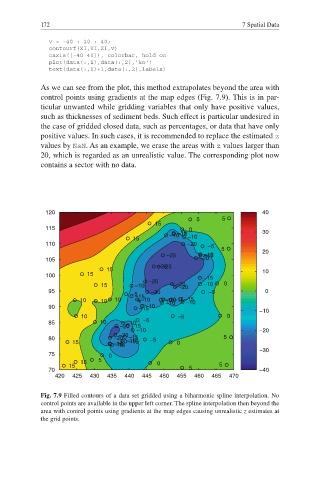
As we can see from the plot, this method extrapolates beyond the area with
control points using gradients at the map edges (Fig. 7.9). This is in par-
ticular unwanted while gridding variables that only have positive values,
such as thicknesses of sediment beds. Such effect is particular undesired in
the case of gridded closed data, such as percentages, or data that have only
positive values. In such cases, it is recommended to replace the estimated z
values by NaN. As an example, we erase the areas with z values larger than
20, which is regarded as an unrealistic value. The corresponding plot now
contains a sector with no data.
120 40
5 5
15
115 0 30
–15
–10 –15 –10
15
110 –20
–5
5 20
–15
–25 –10
105 –20
–25
–25
15 10
100 15 –15
–20
15 –10 –20 –10 0
–20
95 –20 –5 0
–5 –15
–10
10 10 10 –10 –10–15–15
–10
–10
90 –15 –10 ï10
10 –5 0
85 10 –10 –5
–20 –15
–10 ï20
–20
80 –20 –15 –5 5
–15
15 –15 –10 0
–15
–15
ï30
75 0
15 5 0
15 5
70 5 ï40
420 425 430 435 440 445 450 455 460 465 470
Fig. 7.9 Filled contours of a data set gridded using a biharmonic spline interpolation. No
control points are available in the upper left corner. The spline interpolation then beyond the
area with control points using gradients at the map edges causing unrealistic z estimates at
the grid points.