Page 259 - MEMS Mechanical Sensors
P. 259
248 Flow Sensors
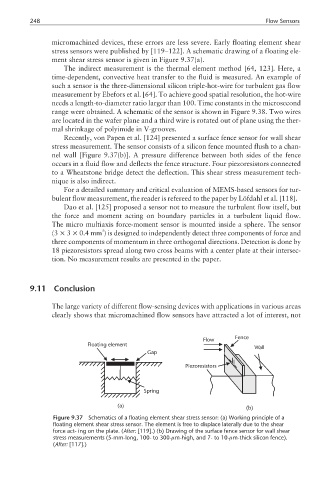
micromachined devices, these errors are less severe. Early floating element shear
stress sensors were published by [119–122]. A schematic drawing of a floating ele-
ment shear stress sensor is given in Figure 9.37(a).
The indirect measurement is the thermal element method [64, 123]. Here, a
time-dependent, convective heat transfer to the fluid is measured. An example of
such a sensor is the three-dimensional silicon triple-hot-wire for turbulent gas flow
measurement by Ebefors et al. [64]. To achieve good spatial resolution, the hot-wire
needs a length-to-diameter ratio larger than 100. Time constants in the microsecond
range were obtained. A schematic of the sensor is shown in Figure 9.38. Two wires
are located in the wafer plane and a third wire is rotated out of plane using the ther-
mal shrinkage of polyimide in V-grooves.
Recently, von Papen et al. [124] presented a surface fence sensor for wall shear
stress measurement. The sensor consists of a silicon fence mounted flush to a chan-
nel wall [Figure 9.37(b)]. A pressure difference between both sides of the fence
occurs in a fluid flow and deflects the fence structure. Four piezoresistors connected
to a Wheatstone bridge detect the deflection. This shear stress measurement tech-
nique is also indirect.
For a detailed summary and critical evaluation of MEMS-based sensors for tur-
bulent flow measurement, the reader is refereed to the paper by Löfdahl et al. [118].
Dao et al. [125] proposed a sensor not to measure the turbulent flow itself, but
the force and moment acting on boundary particles in a turbulent liquid flow.
The micro multiaxis force-moment sensor is mounted inside a sphere. The sensor
3
(3 × 3 × 0.4 mm ) is designed to independently detect three components of force and
three components of momentum in three orthogonal directions. Detection is done by
18 piezoresistors spread along two cross beams with a center plate at their intersec-
tion. No measurement results are presented in the paper.
9.11 Conclusion
The large variety of different flow-sensing devices with applications in various areas
clearly shows that micromachined flow sensors have attracted a lot of interest, not
Flow Fence
Floating element
Wall
Gap
Piezoresistors
Spring
(a) (b)
Figure 9.37 Schematics of a floating element shear stress sensor: (a) Working principle of a
floating element shear stress sensor. The element is free to displace laterally due to the shear
force act- ing on the plate. (After: [119].) (b) Drawing of the surface fence sensor for wall shear
stress measurements (5-mm-long, 100- to 300-µm-high, and 7- to 10-µm-thick silicon fence).
(After: [117].)